TIG welder duty cycle indicates how long the welder runs efficiently at a given amperage without needing to cool down. This feature is significant for all welding projects and it shouldn’t be overlooked, particularly for prolonged tasks. It affects welding performance and results, and ultimately, welders can ensure less downtime and optimal outputs.
We’re here to explore some important points about TIG welders and their duty cycles. Keep reading and you’ll learn the importance of duty cycle and how to choose the best duty cycle for TIG welder.
What Is Duty Cycle in TIG Welding?
To understand what is TIG welder duty cycle is also to understand what is duty cycle in welding. The duty cycle in TIG welding is the percentage of time a welder can operate at a specific power level before facing a cool-down period. To make it clear, a TIG welder is marked with a 70% duty cycle at 125 amps which means that the machine can work continuously for 7 minutes and requires a cool-down period of 3 minutes.
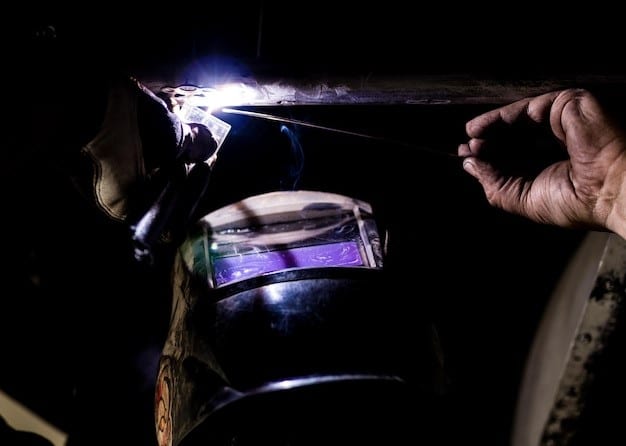

So, the percentage is counted on the 10 minutes cycle. The duty cycle applies to various welding needs. Here we can check some areas where the duty cycle plays a significant role.
- Continuous Operation
- Duty Cycle Relations
- Equipment Durability
- Application Demands
- Cooling Mechanisms
1. Continuous Operation: A lower duty cycle prevents continuous workflow, thus it affects weld quality. A TIG welder with a high-duty cycle ensures longer operations even with thin materials for precision welds.
2. Duty Cycle Relations: If the welder requires higher power levels, it will need more frequent breaks to cool down. The low power level comes with a longer duty cycle to work for light welding projects. A welder with a high power level and sufficient duty cycle help run a long tough welding task.
3. Equipment Durability: TIG welder suppliers suggested that a professional welder shouldn’t work with the TIG welder beyond its rated duty cycle. The duty cycle impacts the machine’s durability. Overworking can produce more heat, shorten the machine’s lifespan, and reduce reliability.
4. Application Demands: Welding in automotive and industrial fabrication requires high-duty cycles for uninterrupted operation. A lower duty cycle may be enough for occasional and shorter tasks.
5. Cooling Mechanisms: TIG welders with higher duty cycles are often equipped with air or water-cooling systems. Welding machines designed for professional application use a water-cooling mechanism to manage heat. Therefore, a welder can smoothly work for a long period with a higher duty cycle if it is managed properly with the right cooling system.
Why Duty Cycle Matters in TIG Welding?
The duty cycle is not a part of the TIG welder machine but it’s an important factor that determines how the machine will work and what the result will be. In a TIG welder, duty cycle influences:
- Machine Performance
- Weld Quality
1. Machine Performance
The duty cycle directly affects the time of continuous operation without producing heat. Overheating due to the use beyond the rated TIG welder duty cycle can damage the equipment. It can lead to component damage, automatic shutdown, and permanent damage to the welder.
Heavy fabrication and industrial projects require prolonged use of the TIG welder at higher amperages. A higher-duty cycle works for extended welds with a fewer break. So, the duty cycle influences workflow efficiency. Low-duty cycle offers less productivity than high-duty cycle welder.
2. Weld Quality
Steady and uninterrupted arcs from the TIG welder are essential for precise welds on delicate materials. A high duty cycle welder provides smooth and continuous arcs for uniform welds. Frequent interruptions for cooling breaks can lead to uneven welds, and it happens when the duty cycle is low.
Using a welder beyond the duty cycle causes fluctuations in arc quality. The extra heat destroys arc stability which results in low-quality welds.
TIG welding offers visually appealing welds with minimal spatter. A welder with the right duty cycle maintains a steady amperage without overheating. It allows for consistent welds and minimal distortion.
How to Calculate and Interpret Duty Cycle in TIG Welders?
When working with a machine, it’s important to know its ins and outs. It will help to operate the machine properly and get the best results. For TIG welder, when you know the duty cycle, you can protect the machine from overheating and enjoy its best.

Calculating the Duty Cycle
The duty cycle is a percentage amount of work and breaks. It’s based on 10-minute intervals. The duty cycle calculation is like the following:
Duty Cycle (%) = (Operating Time / 10 minutes) × 100%
To understand the calculation, let’s consider a welding machine with a 50% duty cycle at 150 amps. It means that the machine can run without any hassle for 5 minutes (50% of 10 minutes) at the specified amperage. After the running period, it requires a cooling period of 5 minutes to prevent overheating.
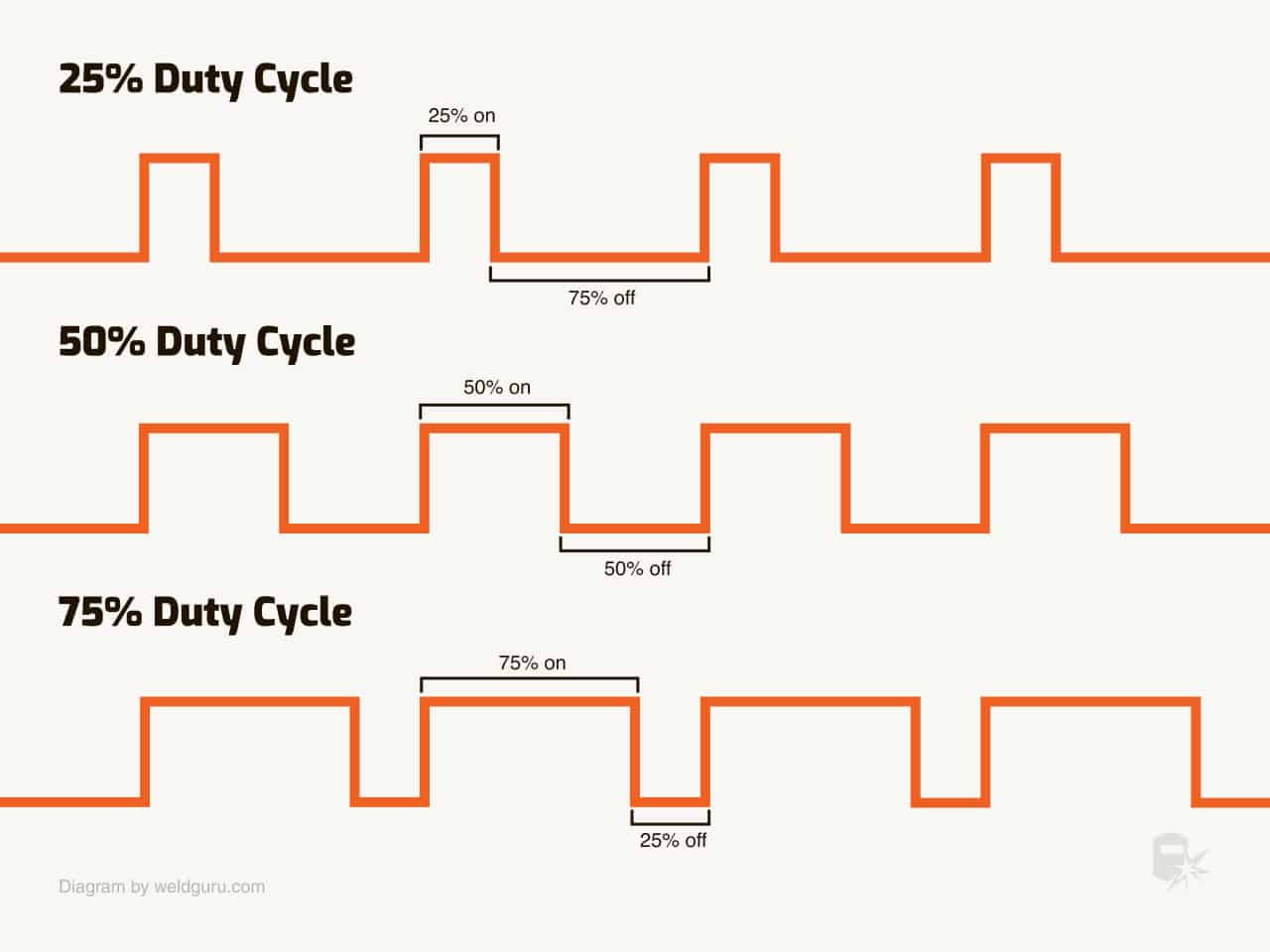
Increasing the amperage above the mentioned level decreases the duty cycle. This explores that at higher amperage, the welder will need more frequent breaks.
Lowering the amperage level increases the duty cycle, allowing for continuous use without cooling down. Some modern welders are designed to run longer with lower amperages continuously.
Manufacturers usually test and fix the duty cycle at a very specific temperature level. So, the duty cycle rating can be changed in the real-world environment. Higher temperatures and poor ventilation can lower the duty cycle.
To obtain the actual efficiency from your TIG welder, make sure you use it in a well-ventilated area. For extended welds, a higher duty-cycle will be convenient. For your quick and shorter welds, a welder with a lower duty-cycle can work properly.
How to Choose the Best Duty Cycle for TIG Welders?
Depending on the project requirements and users’ demands, the selection of a TIG welder with the correct duty cycle can be varied. Here’s a guide to select the best duty cycle TIG welder for your needs.

1. Project Requirements
For occasional use at home, a TIG welder with a maximum 50% duty cycle can work well. For moderate, the duty cycle should be around 60%. When a welder is used for heavy-duty tasks, the duty cycle should be increased up to 100%.
2. Materials and Thicknesses
Welding thin materials requires lower amperages. In this case, a TIG welder with a duty cycle of 20–40% at lower amps is sufficient. For welding thick materials, you’ll need higher amperage settings with 60% or higher duty cycle.
3. Duty Cycle and Welding Time
If your tasks require continuous welds, you will need to use a high-duty cycle TIG welder. For short welds, welders with a 20% to 40% duty cycle will work fine.
4. Amperage Adjustability
Choose a welder with a duty cycle that offers sufficient working time at your expected amperage. For heavy tasks that require higher amperages, select a TIG welder that maintains a high-duty cycle at these settings.
5. A Suitable Cooling System
The cooling system affects a welder’s duty cycle capability. Air-cooled welders are suitable for light welding tasks. Heavy-duty welders for industrial use come with water-cooling features.
Duty Cycle with Different Application Requirements

Not all the welders do the same work. They select welding machines for particular applications. The duty cycle in TIG welding should match the work type for maximum productivity. This helps them to complete their tasks properly.
1. Heavy-duty Use
Welders for industrial use generally work for a longer time. So, opt for high duty cycle machines that require a few breaks in the whole operation. Cooling systems like water-cooled features will lessen the heat produced.
Some TIG welders can offer up to a 100% duty cycle. Make sure to select one with at least 60% duty cycle so that the long tasks can be easier.
2. Moderate-duty Fabrication
Pick a welder with a mid-range duty cycle with desired amperages for moderate-duty applications. Manufacturers who produce medium-sized parts need welders with a 40–60% duty cycle. TIG welders with a 50% duty cycle are suitable for moderate fabrications.
3. Light Repair Work
A TIG welder with a 20–40% duty cycle can complete light repair, fabrication, and maintenance work. In general, light works don’t need a long time welding. So, low or mid-level welders can be sufficient for these tasks.
4. Hobbyist Welding
Hobbyists work on short-term occasional projects. Home projects include low-amperage welds and quick repairs. So, machines have options to take frequent breaks in projects. For all home uses, choose a welder with a 20–30% duty cycle.
5. Automotive Use
Automotive application often requires high amperages. However, many tasks can also be done at moderate amperages. So, the recommended duty cycle of a TIG welder for automotive use is 40-60%. Simpler repairs can require 40% amperages and fabricating requires about 60% duty cycle.
Maximize TIG Welders’ Performance
Focus on a few key practices that enhance the TIG welder’s efficiency and overall welding quality. Make sure to follow the following tips.
1. Match amperage to your job. The right amperage keeps the TIG welder efficient for a long time and you get precise welding always.
2. Utilize appropriate tungsten welding electrodes with the right types and diameter. It helps ensure stable arcs and controlled heat.
3. Clean the metal surfaces with a wire brush to remove contaminants. This will improve arc stability and penetration.
4. Optimize gas flow for different environments. Ensure higher gas flow and avoid excess gas when welding thick materials.
5. Overheating can damage the welder. So, it’s important to ensure a cooling system with your welder. Many TIG welders currently come with water cooling systems to manage excess heat.
6. To get the best results from your welding machine, inspect and clean it regularly. Clean the torch and tungsten electrode to remove debris.
7. Practice to control the machine correctly. Control the foot pedal precisely and learn when to start and stop.
Final Thoughts
To get the most out of a TIG welder, paying attention to the overall quality of the machine makes a huge difference in performance. As a hobbyist or a professional user, you always want the best welding machines and fresh welds.
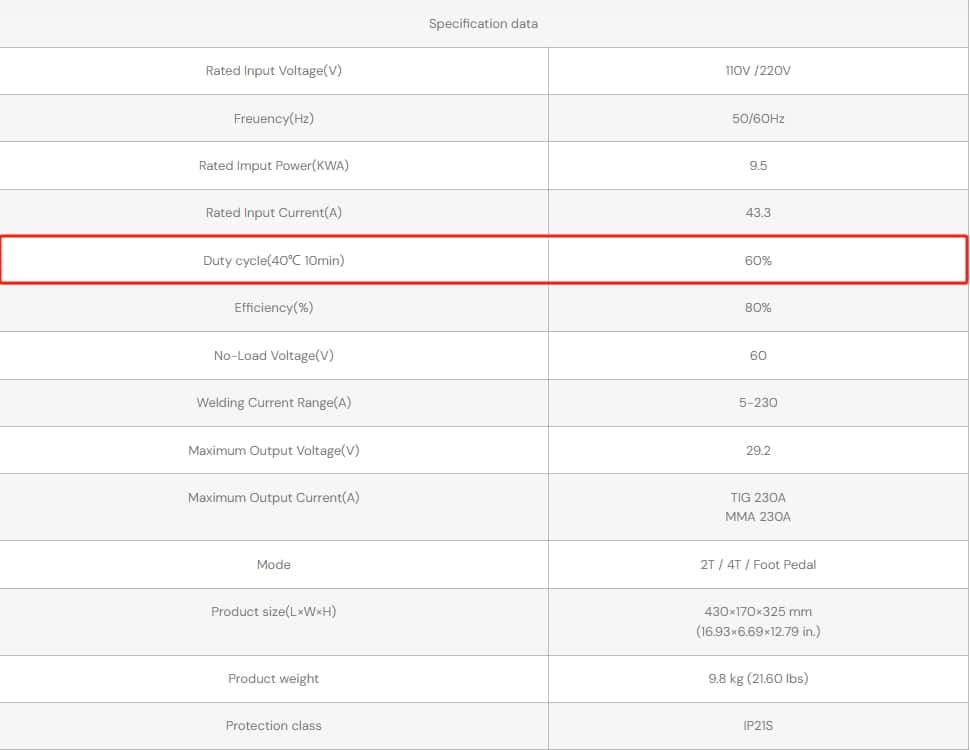
For those looking to own top-quality welding machines, YesWelder is a reliable supplier worth considering. Known for its innovative welding equipment, the company offers a wide variety of TIG welders and accessories designed for professionals and hobbyists. With the 60% TIG welder duty cycle, YesWelder provides each task with reliable outcomes.
FAQs
How can you improve the TIG welder duty cycle?
The duty cycle is fixed by the manufacturer and cannot be changed later. However, you can keep the machine reliable by managing the duty cycle properly. Use the machine at the specified amperage level to prevent heat buildup. Using a cooling system also helps improve the duty cycle.
What is the range for TIG welders’ duty cycle?
TIG welders come with the duty cycles ranging from 20% to 100%. Lower-end models used by DIY enthusiasts have duty cycles of around 20-40%. Professional welders have high-duty cycles ranging from 60 to 100%.
Can you weld continuously with a 100% duty cycle?
You can continuously use a TIG welding machine with a 100% duty cycle. But you must weld at a low amperage. High amperage welding will always need to cool down to manage extra heat.
What happens if you exceed the duty cycle of a TIG welder?
To keep a TIG welder in good condition, you must follow the duty cycle range. Exceeding the range will increase heat and potentially damage the machine. Most welders will automatically shut off if the duty cycle is exceeded. They require a cool-down period to be active again.