Welding inspection ensures the quality and safety of welds in critical industries like construction, aerospace, and oil & gas. By evaluating welds to meet strict standards, inspectors prevent failures that could lead to costly repairs or safety risks. This guide is a go-to resource for mastering welding inspection.
Beginner’s Glossary
| WPS (Welding Procedure Specification) | Instructions for creating a weld. |
| PQR (Procedure Qualification Record) | Documentation of weld test results. |
| NDT (Non-Destructive Testing) | Non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic or radiographic testing. |
What Is Welding Inspection and Why Is It Important?
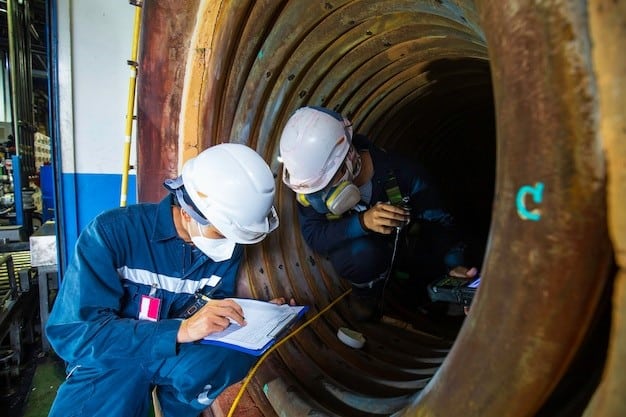

Welding inspection evaluates welds to ensure they meet quality, safety, and regulatory standards, such as AWS D1.1. Inspectors identify imperfections like cracks or porosity that could weaken structures. This process is critical in industries where weld failures could cause disasters, such as building collapses or pipeline leaks.
Key Roles
- Weld Inspectors: Perform visual and non-destructive testing (NDT).
- QA/QC Engineers: Ensure compliance with standards.
- NDT Technicians: Specialize in advanced methods like welding and ultrasonic inspection.
Applications
- Construction (e.g., steel frameworks)
- Aerospace (e.g., aircraft components)
- Oil & Gas (e.g., pipelines)
- Automotive (e.g., vehicle frames)
- Shipbuilding (e.g., hulls)
Common Weld Imperfections
- Cracks: Fractures in the weld or base metal.
- Porosity: Gas pockets weakening the weld.
- Slag Inclusions: Non-metallic material trapped in the weld.
- Lack of Fusion: Incomplete bonding between weld and base metal.
Standards and Codes
- AWS D1.1: Structural welding code for steel.
- ASME Section IX: Boiler and pressure vessel welding.
- ISO 3834: Quality requirements for fusion welding.
Types of Welding Inspection Methods
Welding inspection uses destructive testing (DT) and non-destructive testing (NDT) to assess weld quality. Here’s an overview of key methods:
Visual Weld Inspection
Visual weld inspection is the simplest method, involving examination of welds with the naked eye or magnifying tools to detect surface defects like cracks, undercuts, or irregular bead shapes.
1. Tools: Fillet weld gauges, magnifying glasses, borescopes.
2. Pros: Quick, affordable, no specialized training needed.
3. Cons: Limited to surface defects; cannot detect internal flaws.
4. Best Practices:
- Use bright lighting (500+ lux) and proper angles.
- Measure weld dimensions with gauges.
- Document findings with photos or weld inspection software.
Welding Ultrasonic Inspection
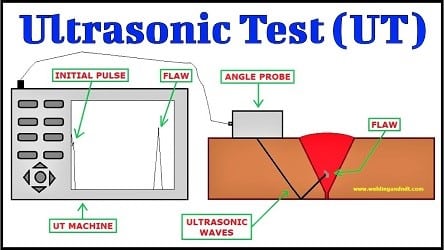
Welding ultrasonic inspection uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal defects, such as voids, cracks, or inclusions, ideal for critical applications.
1. Tools: Ultrasonic testing (UT) devices, transducers.
2. Pros: Highly accurate for subsurface flaws; non-invasive.
3. Cons: Requires trained operators and specialized equipment from welding suppliers.
4. Best Practices:
- Calibrate equipment before use.
- Apply couplant gel for better sound transmission.
- Cross-check findings with radiographic testing (RT) for accuracy.
Other NDT Methods
- Radiographic Testing (RT): Uses X-rays or gamma rays to reveal internal defects. Suitable for thick welds but requires radiation safety measures.
- Magnetic Particle Testing (MT): Detects surface and near-surface defects in ferromagnetic materials using magnetic fields and iron particles.
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT): Identifies surface-breaking defects by applying a dye that seeps into cracks, visible under UV light.
Destructive Testing
- Methods: Bend tests, tensile tests, macro-etching.
- Purpose: Physically test weld strength, used for welder qualification or material validation.
- When Used: During initial procedure qualification (PQR) or random sampling.
What Are the Benefits of Mastering Welding Inspection?
Mastering welding inspection offers significant advantages for your career and industry contributions:
- Career Advancement: Certified inspectors access high-demand roles like QA/QC engineers or NDT technicians, with opportunities for leadership positions.
- Industry Impact: Your skills ensure welds in structures like bridges or pipelines are safe and compliant, reducing the risk of failures.
- Versatility: Expertise in visual weld inspection and welding ultrasonic inspection applies across sectors, from automotive to shipbuilding, allowing specialization or flexibility.
- Professional Credibility: Earning a welding inspection certification establishes you as a trusted expert, boosting confidence among employers and clients.
Top Welding Inspection Tools
Accurate inspections depend on the right welding inspection tools, from manual gauges to advanced devices. We’ve collected some useful tools to consider.
Manual Tools
- Fillet Weld Gauges: Measure weld size and throat thickness.
- Calipers: Verify weld dimensions with precision.
- Magnifying Glasses: Enhance visibility for visual weld inspection.
- Use Case: A construction inspector uses a fillet weld gauge to check weld sizes on a building’s steel frame.
Advanced Tools
- Ultrasonic Testing Devices: Portable UT units for welding ultrasonic inspection.
- Borescopes: Inspect welds in confined spaces, like inside pipelines.
- Laser Displacement Sensors: Measure weld profiles automatically for high-volume production.
- Use Case: An aerospace inspector uses a borescope to examine welds inside an engine casing.
Tool Selection Guide
| Tool | Application | Best For |
| Fillet Weld Gauge | Measuring weld size | Visual weld inspection |
| Ultrasonic Device | Detecting internal defects | Welding ultrasonic inspection |
| Borescope | Confined space inspection | Oil & gas, aerospace |
| Laser Sensor | Automated measurements | Automotive, manufacturing |
Maintenance Tips
- Calibrate UT devices regularly for accuracy.
- Store tools in dry, dust-free cases.
- Clean lenses on borescopes and magnifying glasses after use.
Welding Inspection Technology
Modern welding inspection technology improves efficiency, accuracy, and safety. Get to know how innovation is shaping the field.
Automated Inspection Systems
Robotics and laser-based systems measure weld profiles and detect defects automatically. They have faster inspections, consistent results, reduced human error.
Drone-Based Inspection
Drones navigate confined or hazardous areas (e.g., tanks, pipelines) to capture high-resolution weld images. This has safer inspections, access to hard-to-reach areas.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI analyzes weld images or UT data to identify defects with high accuracy. In the future, AI may operate predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring.
Weld Inspection Software
Software platforms for data logging, defect tracking, and reporting.
Features:
- Compliance record management.
- Visual defect reports.
- Integration with UT or RT devices.
Comparison
| Software Type | Key Features | Best For |
| Cloud-Based | Remote access, defect tracking | Large-scale projects |
| Image Analysis | UT integration, detailed visual reporting | Aerospace, R&D teams |
| Custom QA/QC | Tailored reporting, compliance tools | Enterprise-level usage |
Welding Inspection Certification
A welding inspection certification validates expertise and enhances career opportunities. Here are the top options. You can also see other types of welding certifications in another article.

Key Certifications
- AWS Certified Welding Inspector (CWI): Globally recognized, career advancement.
- CSWIP: Offers levels for visual and NDT inspections, widely accepted internationally.
- ASNT Level III: For NDT specialists, focusing on methods like welding ultrasonic inspection.
How to Get Certified
- Assess Eligibility: Confirm experience requirements (e.g., years in welding or inspection).
- Enroll in Training: Attend seminars, courses, or online programs focused on NDT and standards.
- Prepare for Exams: Study AWS D1.1, practice visual inspections, and use UT simulators.
- Pass the Exam: Schedule through certification bodies; expect multiple sections.
- Maintain Certification: Renew periodically with continuing education or retesting.
FAQs about Welding Inspection Certification
How long does CWI certification take?
Several months with training and exam prep.
Can beginners pursue certifications?
Yes, start with associate-level certifications.
Industry-Specific Welding Inspection
Welding inspection varies by industry, with tailored methods and standards.
Aerospace: High-precision NDT (RT, welding ultrasonic inspection) for safety-critical welds.
Oil & Gas: Drones and UT for pipeline inspections; RT for pressure vessels.
Construction: Visual weld inspection and MT for structural steel.
Automotive: Automated laser systems for mass production.
How to Get Started with Getting Welding Inspection Certification
New to welding inspection? Follow these steps to begin!

Step 1: Build Foundational Knowledge
- Learn welding basics (MIG, TIG, stick) to understand weld creation.
- Learn the features of MIG, TIG, and Stick welding machines.
- Study weld imperfections and standards (AWS D1.1, ASME Section IX).
Step 2: Gain Practical Experience
- Work as a welder or apprentice to observe welds.
- Shadow inspectors on construction or pipeline projects.
- Tip: Volunteer for QA/QC tasks to learn inspection workflows.
Step 3: Start with Visual Weld Inspection
- Why: Easiest entry point, requires minimal tools.
- Tools: Fillet weld gauges, magnifying glass.
- Practice: Inspect sample welds for cracks or irregular beads.
Step 4: Pursue Training
- Enroll in NDT courses (e.g., UT, RT) through professional organizations.
- Attend certification prep seminars.
- Focus: Practical skills and standard compliance.
Step 5: Get Certified
- Start with entry-level certifications (e.g., associate-level CWI).
- Plan for advanced certifications like CSWIP or ASNT Level II.
- Timeline: 1-2 years from beginner to certified inspector.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Welding Inspection
1: Inadequate Preparation
- Issue: Skipping WPS review leads to missed specification errors.
- Solution: Always verify WPS and PQR before inspecting.
2: Poor Visual Inspection Techniques
- Issue: Missing surface defects due to dim lighting or wrong angles.
- Solution: Use 500+ lux lighting and magnifying tools for visual weld inspection.
3: Misinterpreting Ultrasonic Data
- Issue: Incorrectly identifying defects in welding ultrasonic inspection.
- Solution: Calibrate UT devices and cross-check with RT or MT.
4: Neglecting Tool Maintenance
- Issue: Using uncalibrated welding inspection tools skews results.
- Solution: Calibrate regularly and store in dry cases.
5: Ignoring Documentation
- Issue: Incomplete logs cause audit failures.
- Solution: Use weld inspection software for accurate reporting.
6: Overlooking Safety
- Issue: Not wearing PPE or ignoring confined space protocols.
- Solution: Follow safety guidelines; use drones for hazardous areas.
Tips for Success
- Double-check findings with a second method (e.g., visual + UT).
- Attend regular training to stay updated on standards.
- Start with visual inspections to build confidence.
- Learn one NDT method (e.g., UT) before tackling others.
Final Thoughts
Welding inspection ensures the safety and reliability of welds in critical applications, from buildings to aircraft. By mastering visual weld inspection, welding ultrasonic inspection, and modern welding inspection technology, one can build a rewarding career and contribute to industry safety.
Recommended Reading
1. AWS D1.1



