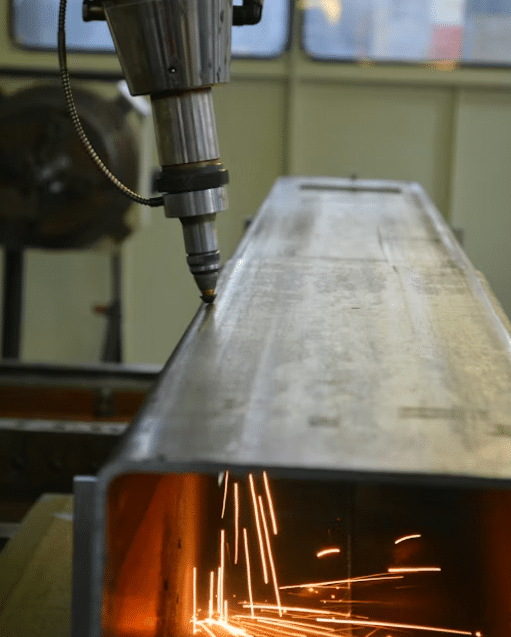
Welding is all about connection, and the quality of that connection often depends on one critical component: the welding wire. Among the many types available, copper welding wire stands out as one of the most reliable and versatile options in the industry.
Used across various applications, including electrical, automotive, HVAC, and heavy fabrication, copper welding wire offers excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance, and smooth arc performance. Whether you’re joining copper components or working with steel, choosing the right copper-based wire can make all the difference in the strength, appearance, and longevity of your welds.
This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about copper welding wire, including how it works, where it’s used, and why it remains a top choice for both professionals and hobbyists.
What Is Copper Welding Wire?
Copper welding wire refers to either solid or coated welding wire that contains copper or has a copper layer on its surface.
There are two main categories:
- Copper-Coated Steel Wire: The most common type used in MIG welding. The steel core is coated with a thin layer of copper to enhance electrical conductivity, improve arc stability, and increase corrosion resistance.
- Pure Copper or Copper Alloy Wire: Used for welding copper, bronze, or brass materials. These wires have high conductivity and are ideal for applications involving electrical components and heat exchangers.
In simple terms, copper in the wire ensures smooth current flow and prevents oxidation, leading to cleaner, stronger welds.
Why Copper Coating Matters
In welding, stable electrical contact between the wire and the contact tip is critical. Copper coating plays a major role in achieving that.
1. Enhanced Electrical Conductivity
Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity. A thin copper layer allows efficient current transfer from the welding gun to the wire, ensuring a consistent and stable arc, especially when buying from a welding supply company.
2. Better Feeding Through the Torch
The smooth, copper-coated surface reduces friction between the wire and liner, allowing it to feed evenly through the gun without snagging, which is especially important in automated or high-speed MIG welding setups.
3. Corrosion Protection
Uncoated wires are prone to oxidation when exposed to air. A copper coating protects the wire from rust and moisture, thereby extending its shelf life and performance.
4. Improved Arc Stability
Copper helps maintain a steady electrical connection, resulting in smoother arcs, minimal spatter, and cleaner weld beads.
Types of Copper Welding Wires
Depending on your base material and process, you’ll encounter several types of copper-based welding wires:
1. Copper-Coated Mild Steel Wire (ER70S-6)
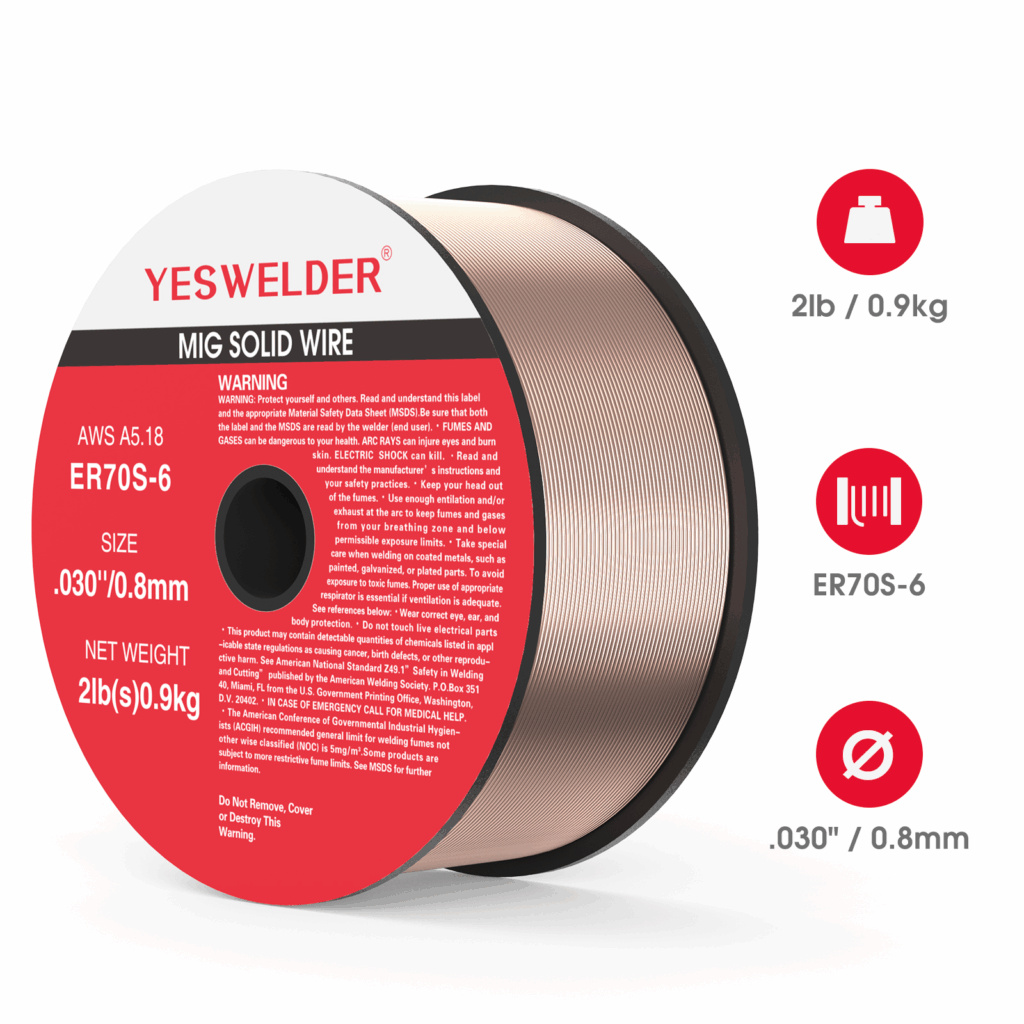
- Most widely used in MIG welding.
- Designed for carbon steel and mild steel.
- Offers good penetration and smooth arc characteristics.
- Suitable for welding rusty or dirty metal surfaces.
2. Copper-Silicon Alloy Wire (ERCuSi-A)
- Known as silicon bronze wire.
- Excellent for joining dissimilar metals or thin sheets.
- Commonly used in automotive repairs, HVAC systems, and sheet metal fabrication.
- Produces clean, attractive welds with minimal spatter.
3. Pure Copper Wire (ERCu)
- Used for welding pure copper and copper alloys.
- Offers outstanding electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Common in electrical busbars, motors, and plumbing.
4. Copper-Nickel Wire (ERCuNi)
- Combines copper’s conductivity with nickel’s strength and corrosion resistance.
- Ideal for marine and desalination systems due to its resistance to seawater corrosion.
Applications of Copper Welding Wire
Due to its conductivity, corrosion resistance, and versatility, copper welding wire is utilised in a wide range of industries.
1. Automotive Manufacturing
Used to join body panels, exhaust systems, and frames, especially in areas requiring dissimilar metal welding or resistance to corrosion.
2. Electrical and Power Systems
Perfect for welding busbars, conductors, and electrical connectors where conductivity is critical.
3. HVAC and Plumbing
Silicon bronze and copper alloy wires are used for leak-proof joints in refrigeration, air-conditioning systems, and copper pipes.
4. Shipbuilding and Marine
Copper-nickel wires are preferred for their durability in harsh saltwater environments.
5. Industrial Fabrication
Used in machinery, tools, and pressure vessels that need a combination of strength and conductivity.
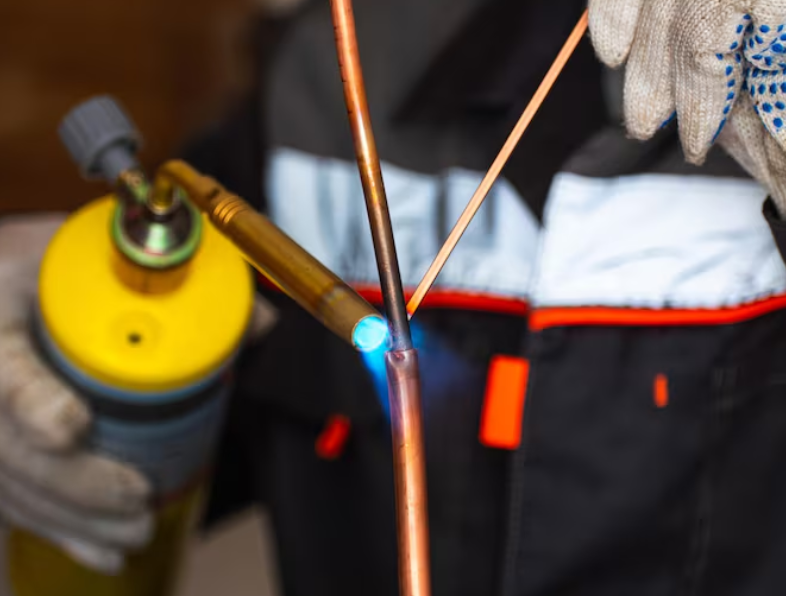

Advantages of Copper Welding Wire
1. Excellent Conductivity
Whether you’re welding copper components or using mig welding wire, the high electrical conductivity ensures stable arc performance and better penetration.
2. Reduced Spatter
The smoother arc and steady current flow minimize spatter, leading to less cleanup and higher-quality finishes.
3. Long Shelf Life
Copper coating resists corrosion, allowing the wire to last longer — even in humid environments.
4. Versatility
Copper-based wires can join a variety of metals, from mild steel to brass, making them suitable for multiple welding applications.
5. Enhanced Feedability
The smooth copper surface improves wire feeding through liners and contact tips, reducing downtime and wire burn-back.
6. Attractive Weld Appearance
Especially with silicon bronze wire, the final bead often has a golden, polished finish, perfect for decorative or visible welds.
Disadvantages and Considerations
While copper welding wire offers multiple advantages, it’s not always the best fit for every project.
1. Cost
Copper-coated wires are slightly more expensive than uncoated ones due to the coating process and material costs.
2. Copper Flaking
In some lower-quality wires, the copper layer can flake off and accumulate in the liner, leading to feeding issues. Always choose premium-quality wires to avoid this.
3. Overheating Risk
In some cases, the copper coating can increase heat transfer to the contact tip, leading to premature wear during prolonged weld cycles.
4. Not for Aluminum
Copper wire should not be used for aluminum welding. The two metals have vastly different melting points and exhibit significant chemical incompatibility issues.
Best Welding Processes for Copper Wires
1. MIG Welding (GMAW)
- The most common process for copper-coated steel wires.
- Provides fast, efficient, and clean welds.
- Works well with argon-CO2 mixtures.
2. TIG Welding (GTAW)
- Best for thin copper or copper alloys.
- Offers precise control and cleaner welds with minimal oxidation.
- Typically uses pure argon or argon-helium mixtures.
3. Brazing
- Silicon bronze wires (ERCuSi-A) are often used for brazing steel or galvanized steel.
- Ideal for thin sheet metal and auto bodywork where heat distortion must be avoided.
Safety Considerations
Welding with copper wires is generally safe, but always follow these precautions:
- Use adequate ventilation to avoid inhaling copper oxide fumes.
- Always wear auto-darkening helmets and heat-resistant gloves.
- Avoid touching bare copper wires with oily hands, it can lead to contamination.
- Keep your workspace dry and clean to prevent electrical hazards.
Copper welding wire is more than just a conductor, it’s a performance booster that improves weld quality, consistency, and durability. Whether you’re joining copper pipes, repairing automotive panels, or fabricating steel structures, copper-coated or alloy wires deliver excellent results across a variety of applications.
Their combination of conductivity, corrosion resistance, and stability makes them indispensable in modern fabrication shops and industrial environments.
So, the next time you’re setting up your welder, remember, choosing the right copper welding wire isn’t just about the coating; it’s about ensuring the perfect connection every single time.
FAQs: Copper Welding Wire Explained
Copper welding wire should not be used for welding aluminum. The two metals have different melting points and chemical incompatibilities, which make them unsuitable for welding with copper wire. For aluminum, it’s better to use aluminum-specific welding wire.
Copper coating enhances the electrical conductivity of MIG welding wire, leading to a stable arc and better penetration. It also reduces friction during feeding and improves the overall performance of the welder machine.
Silicon bronze copper welding wire is ideal for automotive repairs because it allows for clean, attractive welds with minimal spatter. It’s especially useful when joining dissimilar metals, making it highly effective for welding automotive body panels and other metal components.