TIG welding is a universal and precise method utilized across various industries. This process includes creating an electric arc between a non-consumable tungsten electrode and the workpiece, shielded by an inert gas, typically argon. The process is renowned for producing high-quality welds, making it ideal for applications requiring strong and clean joints.
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and power plants commonly employ TIG welder machine because TIG welders handle thin and delicate materials with minimal distortion. Understanding TIG welding’s fundamentals is crucial for leveraging its full potential in specialized applications.
Methods of Arc Starting
Scratch Start
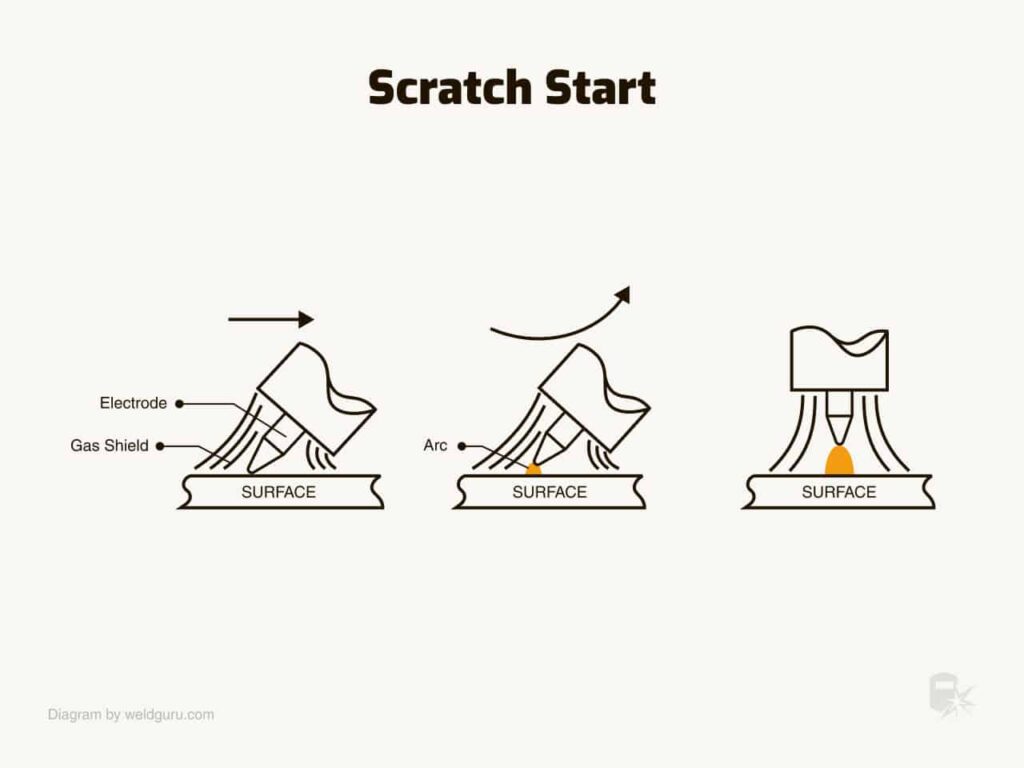
Image credit: https://weldguru.com/scratch-start-tig-vs-lift-arc/
Scratch start is a basic method used in TIG welding to initiate the arc. In this technique, the welder drags the tungsten electrode across the workpiece, similar to striking a match, and then lifts it to form the arc. This simple method doesn’t require additional equipment, making it accessible for beginners. However, it may cause contamination of the tungsten and the weld pool, leading to potential weld defects. Experienced welders can minimize contamination in scratch start by using a clean, sharpened tungsten and a swift motion to establish the arc.
Lift TIG
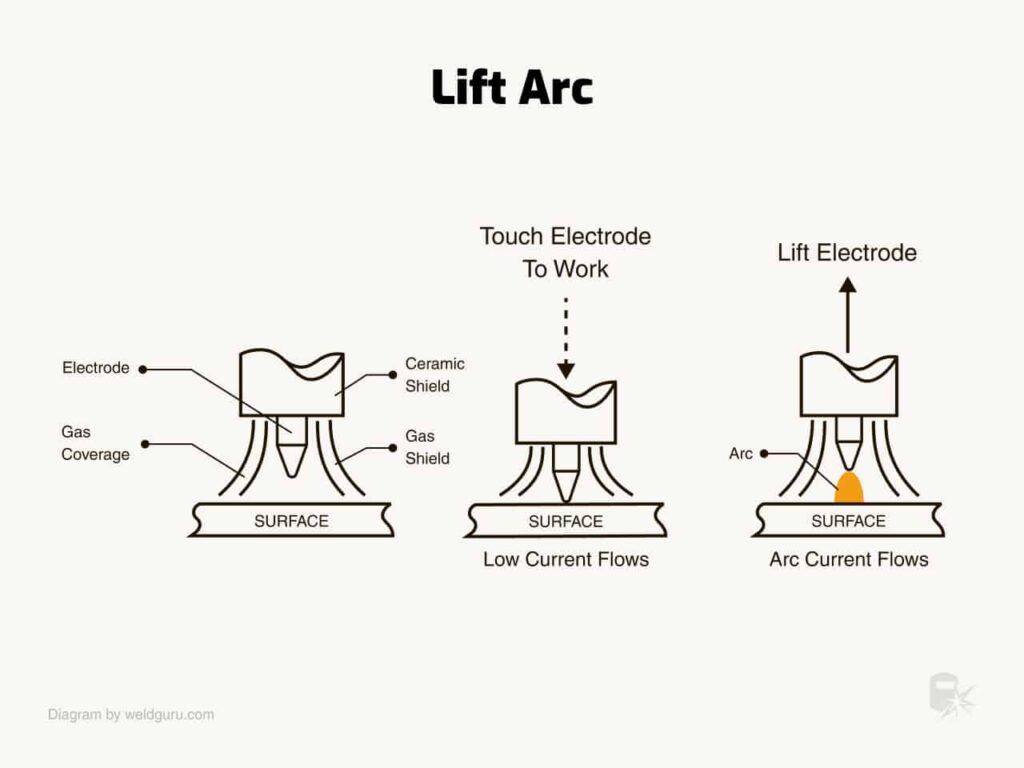
Image credit: https://weldguru.com/scratch-start-tig-vs-lift-arc/
Lift TIG is a more refined method than scratch start. The welder connects the tungsten electrode to the workpiece and lifts it off to initiate the arc. Unlike scratch start, this method minimizes contamination because the arc is established only after the electrode is lifted. Lift TIG provides better control and reduces the risk of damaging the electrode, making it suitable for more precise applications.
High Frequency
High-frequency start involves using a high-frequency generator to create a spark between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece, establishing the arc without physical contact. This method is advantageous as it prevents contamination and electrode wear, allowing for a clean start and consistent arc. The high-frequency start is commonly used in automated TIG welding systems and for welding materials sensitive to contamination, such as aluminum and magnesium. It provides the highest level of precision among the arc-starting methods.
Key Features of TIG Welding
Precision and Control
TIG welding offers unmatched precision and control, allowing welders to produce clean and accurate welds. This process is especially useful for projects requiring fine detail work, as the welder can precisely manage the heat input and filler material. Using a non-consumable tungsten electrode ensures a stable arc and consistent weld quality, which is crucial in industries where high-quality standards are mandatory.
Versatility
The versatility of TIG welding makes it appropriate for a range of materials and applications. It can be utilized on metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, copper, etc. Adjusting parameters such as current type, pulse settings, and electrode size is crucial when welding different metals to achieve high-quality welds. Additionally, TIG welding can handle thick and thin materials, providing flexibility for various welding tasks. The process is also compatible with manual and automated welding setups, making it adaptable to different working environments.
Clean Process
Another key feature of TIG welding is its ability to produce clean welds with minimal spatter and fumes. Using inert gases like argon, helium, or argon-helium mixtures helps protect the weld area from contamination, resulting in high-quality welds that require little to no post-weld cleanup. This clean process is particularly important when working with sensitive materials that impurities can easily compromise.
TIG Welding Applications

Automotive Industry
- Precision and Aesthetic Quality: TIG welding is widely used in the automotive industry for tasks requiring precision and high aesthetic quality. It is perfect for welding thin materials and intricate components, such as exhaust systems, roll cages, and chassis parts.
- Material Compatibility: This welding method suits various metals commonly used in vehicles, including stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. Its versatility allows manufacturers to work with different material combinations.
- Repair and Fabrication: TIG welding is employed to repair and fabricate automotive parts. Its ability to produce strong, clean welds makes it a preferred choice for custom modifications and high-performance components.
Aerospace Industry
- Critical Welds: TIG welding is crucial for creating critical welds on aircraft components in the aerospace sector. The process’s precision and control ensure the structural integrity of parts that withstand extreme conditions.
- Material Versatility: Aerospace applications often involve specialized materials like aluminum, magnesium, and titanium, which require careful handling to avoid contamination. TIG welding provides the necessary control to work with these metals.
- High Standards: The aerospace industry demands the highest standards of quality and safety. TIG welding’s ability to produce defect-free welds is essential for meeting these stringent requirements.
Nuclear Facility and Power Plants
- High Integrity Welds: The reliability of welds is paramount in nuclear facilities and power plants. TIG welding produces high-integrity joints that can withstand harsh environments and high pressures.
- Corrosion Resistance: The process is often employed for welding components that require high corrosion resistance, such as pipes and pressure vessels. TIG welding’s ability to create clean, precise welds helps prevent issues like crevice corrosion.
- Specialized Applications: TIG welding is suitable for working with materials like stainless steel and nickel alloys, commonly used in nuclear applications for their durability and resistance to radiation.
Art and Sculpture
- Artistic Flexibility: TIG welding is popular among artists and sculptors for its versatility and precision. It allows for the creation of intricate designs and fine details in metal sculptures.
- Material Variety: Artists can use TIG welding to join various metals, including steel, bronze, and copper. The process’s ability to handle different thicknesses and materials expands creative possibilities.
- Clean Finish: The clean welds produced by TIG welding reduce the need for extensive post-weld finishing, making it more comfortable to achieve the desired aesthetic without compromising the work’s integrity.
Other Applications
- Food and Beverage Industry: TIG welding is often used in the food and beverage industry for fabricating and repairing stainless steel equipment. The process ensures smooth welds that are easy to sanitize, which is crucial for maintaining hygiene standards.
- Medical Equipment: The medical industry utilizes TIG welding to manufacture surgical instruments and medical devices. The precision and cleanliness of TIG welds are vital for providing the safety and functionality of these tools.
- Electronics and Electrical Industry: TIG welding is employed in the electronics industry to join delicate components and materials. Its precise control over heat input minimizes the risk of damaging sensitive electronic parts.
Features and Benefits of TIG Welding in Various Industries
| Industry | Feature | Main Benefits |
| Automotive | Precision Welding | Enables strong, lightweight structures with clean welds, crucial for vehicle safety and performance. |
| Aerospace | High-Quality Welds | Ensures structural integrity and durability of aircraft components under extreme conditions. |
| Nuclear Facilities | Corrosion Resistance | Provides durable, corrosion-resistant joints for safe handling of radioactive materials. |
| Art and Sculpture | Material Versatility | Allows for detailed and intricate work with various metals, enhancing artistic expression. |
| Medical Equipment | Clean Welds | Ensures safe, sterile manufacturing of medical devices. |
| Food and Beverage | Hygienic Welding | Facilitates easy cleaning and maintenance, maintaining hygiene in food processing equipment. |
Advantages of TIG Welding
High-Quality Welds

TIG welding is well-known for producing high-quality welds with a clean finish. The process allows precise control over welding parameters, such as heat input and adding filler material. This control results in welds with minimal spatter and defects, making it ideal for applications where aesthetics and structural integrity are critical. The inert gas shielding used in TIG welding prevents oxidation and contamination, ensuring a clean and strong weld.
Minimal Distortion
Another significant advantage of TIG welding is the minimal distortion it causes to the workpiece. This is especially important when working with thin materials, where excessive heat can lead to warping or deformation. TIG welding allows for fine-tuning of the heat input, reducing the material’s risk of overheating. This precision helps maintain the original shape and dimensions of the workpiece, making it suitable for detailed and intricate projects.
Flexibility in Material Thickness
TIG welding is adaptable and can handle a wide range of material thicknesses. Whether working with very thin sheets or thicker sections, TIG welding provides the necessary control to achieve high-quality welds. This flexibility is due to the welder’s ability to adjust the heat input and use a filler material if needed. The process is compatible with different metals, including steel, aluminum, and more exotic alloys, making it a preferred choice in industries requiring versatility.
Disadvantages of TIG Welding
Higher Skill Requirement
Due to its complexity, TIG welding requires a high level of skill and experience. The welder must precisely control the tungsten electrode and filler material, often simultaneously. This dual control can be challenging, especially for beginners, and requires extensive training and practice to master.
Slower Welding Speed
Compared to other welding methods, TIG welding is relatively slow. The need for precise control and careful application of filler material contributes to a slower process. This can be a disadvantage when time efficiency is critical, as it may increase production time.
Higher Costs
The equipment and consumables used in TIG welding are generally more expensive than those used in other welding processes. Additionally, the need for highly skilled welders can increase labor costs. The slower welding speed also contributes to higher operational costs, making TIG welding a more expensive option in some cases. These factors can limit its use to applications where high-quality welds are essential and justify the additional costs.
Conclusion
High-quality TIG welding equipment is essential for achieving precise and reliable welds, especially in industries where precision and durability are crucial. Investing in advanced TIG welding technology ensures better control and minimal defects, vital for maintaining the integrity of welded structures. It is essential for welders to invest in reputable brands. YesWelder is a reputable supplier of TIG welding equipment, offering various products catering to industrial and personal needs. Their dedication to quality and affordability makes them a trusted choice for welders seeking reliable and efficient welding solutions.
FAQs
What materials can be welded using TIG welding?
TIG welding can be operated on various materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, titanium, and various alloys. This versatility makes it suitable for aerospace, automotive, and art industries.
What are the main advantages of TIG welding over other welding methods?
TIG welding offers several benefits, such as producing high-quality welds with minimal spatter and distortion. It provides precise control over the welding process, making it ideal for detailed work. Additionally, it is suitable for welding thin materials and delicate components.
Is TIG welding suitable for beginners?
While TIG welding provides excellent control and high-quality results, it requires a higher skill level than other methods like MIG or stick welding. Beginners may find it challenging due to the need to manage both the torch and filler material simultaneously and the precise control required over the arc. However, with appropriate training and practice, it can be mastered.



