The welding industry forms the very foundation of manufacturing across the automotive, construction, infrastructure, energy, and aerospace sectors. As one of the most popular techniques for permanently joining metals, welding plays a pivotal role in fabricating innumerable components and end-products.
This article will serve as an extensive guide to the global welding domain – throwing light on the current market size, exponential growth trends, regional analysis, emerging technologies, as well as impediments and future outlook.
We will also assess trends like automation, sustainability, customization, and digital integration in detail.
Current Market Landscape
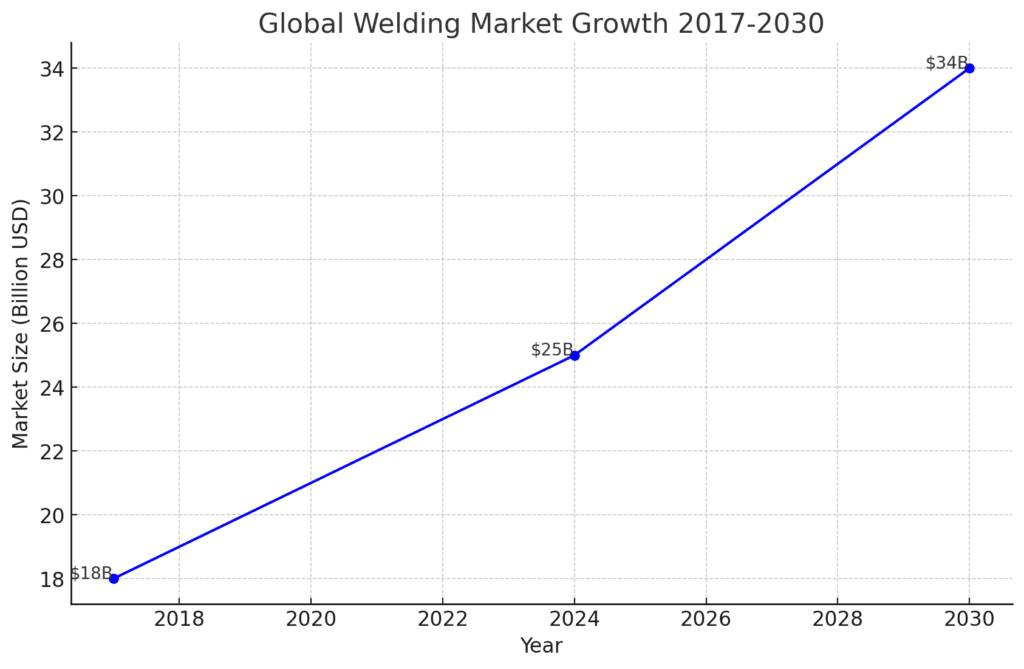
The welding industry stands robust with a market valued at $25 billion globally as of 2024. By 2030, credible estimates indicate that the market is primed to surpass $34 billion. The sector is witnessing an evolutionary transformation catalyzed by high-tech advancements, changing consumer needs, and an upswing across manufacturing verticals.
Market Size and Value
Currently valued at $25 billion, the welding sphere has more than doubled over the last decade, registering a robust 6.2% CAGR from 2017-2023.
Asia Pacific constitutes the most dominant share (36%) trailed by Europe (25%) and North America (22%).
China, India, Japan and South Korea remain pivotal for APAC domain supremacy.
By 2030, the global market valuation is expected to surpass $34 billion – exhibiting a sturdy CAGR upward of 6% through the next decade.
The substantial growth and size of the industry can be attributed to ubiquitous, cost-effective applicability in permanent bonding and joining all kinds of metals across manufacturing realms.
Additionally, favorable governmental initiatives supporting localization are spurring domestic players – attracting foreign investments, and enhancing skill development through dedicated welding institutes. These institutes are churning out high-quality welders – fulfilling increasing sectoral demands and boosting exports globally.
Market Segmentation
The market is segmented into equipment and consumables. Nearly 60% of the market constituted consumables including stick electrodes, solid wires, flux wires, SAW wires, and fluxes in 2024, exhibiting a high CAGR of 5%.
Equipment like welders, jigs & fixtures accounted for the rest. Arc welding forms the most widely deployed technology globally – holding a lion’s share of 42% currently. Other prevailing technologies comprise – resistance welding, oxy-fuel, laser beam, electron beam, etc.
Leading Brands
The market remains highly fragmented with the top 5 players constituting just 20% collectively. Prominent manufacturers and suppliers include:
- Lincoln Electric: Industry leaders renowned for cutting-edge arc and plasma equipment offerings globally. Most popular for stick welders and multi-process welders.
- ESAB: Major Sweden-based company offering high-end MIG/GMAW equipment, consumables like wires, fluxes etc. Known for stick electrodes and quality helmets.
- Kempii: Leading provider of MIG/TIG/stick equipment and solar-driven welders globally. Known for the latest transformer-inverter hybrid welders.
- YesWelder: YesWelder is one of the leading brands focusing on high-cost-effective multifunctional welding machines. Always standing from the user’s standpoint, YesWelder develops products based on user needs. At the same time, it is also expanding in the field of industrial welding machines.
- Miller Electric: Legacy 120-year-old US brand offering premium equipment like MIG, TIG, Arc, and plasma cutters used extensively in the large-scale shipbuilding industry.
While the market remains highly decentralized, the focus is shifting towards enhanced value delivery encompassing automation, integrated IoT features, energy efficiency, and sustainability. As welding finds ubiquitous applications across the transportation, construction, infrastructure, and energy spheres – adjacent markets for gases, automation systems, and safety equipment flourish concurrently.
Market Growth
The global welding industry has witnessed remarkable growth in recent years – driven by significant technological advancements and rapid industrialization across manufacturing sectors. Valued at $25 billion currently, experts predict over 6% yearly growth – exceeding $34 billion by 2030.
Technological Achievements
Several cutting-edge technologies have emerged within welding over the past decade – uplifting efficiency, precision, quality, and safety benchmarks. Increased R&D by leading brands has catalyzed the launch of avant-garde solutions encompassing:
- Automated systems with integrated sensors, IoT capabilities enabling real-time monitoring, minimized human intervention through chatbots and remote troubleshooting.
- Robotics & cobots are deployed extensively for repetitive, hazardous, and complex welding tasks. Collaborative robots work in tandem with human welders – curtailing risks.
- Augmented and virtual reality incorporated in tailored training programs – providing simulated hands-on exposure without hazards. Enables global reach transcending geographical barriers.
- Heightened focus on cleaner technologies visible through solar-powered welders, energy-efficient equipment, reduced reliance on fossil fuels, and lower emissions. Achieving sustainability goals.
- Lightweight and superior alloys, advanced electrodes/wires, and shielding gases developed – delivering impeccable welds suited for high-strength applications across aerospace, defense, energy and automotive domains.
Such developments have bolstered efficiency, safety, and compliance – building customer trust and loyalty.
Industrial Expansion
Upsurge across manufacturing, increasing urbanization, and rising infrastructure projects have spurred welding demand – expanding the industry’s horizons. Favorable governmental initiatives have boosted domestic manufacturing and exports – attracting investments. The establishment of dedicated welding institutes has enhanced skill development – fulfilling sectoral demands.
With EVs gaining precedence along with clean energy projects involving solar, wind, nuclear power etc – the deployment of welding continues to grow ubiquitously. Industry 4.0 trends are steering expansion blending automation, and data-exchange technologies across processes.
As welding applications diversify into new areas, adjacency markets including gases, automation equipment, and safety gear will proliferate in parallel.
Regional Market Analysis
With welding finding widespread applications across pivotal sectors like manufacturing, construction, infrastructure, energy, and transportation – the industry has thrived globally. However, adoption and growth trends have varied across different regions.
North America
North America constitutes nearly 22% of the total welding equipment and consumables market presently. The regional market has expanded at a healthy CAGR of 6% in the last 5 years – crossing USD 5.5 billion valuations in 2022. The growth is attributed to surging demand from enduring manufacturing of automobiles and related components, stable construction activities and ongoing investments in advancing production technologies and facilities.
USA
The US leads the regional market with a lion’s share of 86%. Increasing public infrastructure projects involving highways, tunnels, and metros have spurred welding consumption. Rising popularity and incentives for EVsares propelling related manufacturing. Growing employment opportunities attracting an immigrant workforce has led to a parallel increase in housing projects- furthering welding equipment requirements. However, uncertainties in international trade policies and relations have temporarily slowed market expansion.
Canada
Canada has witnessed augmenting welding demand from its well-established agricultural equipment and aviation sectors. The emergence of several solar/wind energy projects has also contributed to the welding industry’s growth. Favorable initiatives like the Canada- US- Mexico Agreement (CUSMA) have eased cross-border trade boosting fabrication and welding equipment requirements.
The distribution below reflects the current regional contribution:
| Region | Market Share (2024) | Historical CAGR | Estimated Value (2030) |
| North America | 22% | 6% | $8.5 billion |
| South America | 6.5% | 5.4% | $2.2 billion |
| Europe | 25% | 5% | $9.8 billion |
| Asia Pacific | 36% | 6.2% | $14 billion |
| Rest of World | 12% | 6.4% | $4 billion |
South America
South America comprises roughly a 6.5% share of the international welding market. Backed by Brazil’s robust manufacturing, construction, mining, and energy sectors – the region registered a 5.4% CAGR from 2017-24, representing sales over USD 1.5 billion. Economic turmoil in countries like Venezuela and Argentina had initially slowed market progression.
With the recovery in commodity and oil prices, metal and mineral exploration activities have regained momentum – raising demand for welding again. Furthermore, Brazil’s substantial infrastructure investments ahead of the upcoming FIFA World Cup and policies encouraging domestic manufacturing through tax benefits are bolstering the welding industry’s standing.
Europe
Presently exceeding a 25% share of the global welding market, Europe signifies the second largest geography after Asia Pacific. Established industrial sectors spanning automotive, electronics, and construction equipment combined with government stimuli for public infrastructure projects have sustained the consumption of welding technologies and consumables. The European welding market has grown at a respectable CAGR of 5% over the last decade.
Germany leads the European regional market accounting for almost 18% share. The rising electric mobility shift has led automakers to expand investments and manufacturing – boosting welding requirements.
Italy, France, and Spain represent other major demand hotspots witnessing surging welding deployment across efforts to upgrade existing power infrastructure and growing renewable energy projects including solar, wind, and tidal farms.
Asia Pacific (APAC)
The APAC belt accounts for the maximum share of 36% in the global welding market currently. Backed by thriving manufacturing and construction ecosystems across India, China, Japan, and South Korea – APAC registered the highest CAGR upward of 6.2% from 2017-22; crossing USD 9 billion valuations.
Government-backed industrialization efforts have attracted substantial foreign investments- channelling funds into developing welding institutes, and skill training programs and fostering export competencies.
China leads the regional market representing almost half the market share – valued at USD 4.5 billion in 2022. From automotive, and heavy machinery to shipbuilding – China’s competency across major industries while exporting globally has expanded welding consumption manifold.
India remains another principal demand generator given its robust infrastructure pipeline, rising urbanization, and progressive policy reforms to establish the country as an export hub. Strong automotive manufacturing and rapidly growing renewable energy installations also leverage welding technology significantly.
Rest of the World
The regions grouped under Rest of the World (RoW) include the Middle East, Africa and others. Presently these geographies account for roughly 12% of the international welding industry.
Mineral-rich and infrastructure-deficient African and Middle Eastern nations have gained substantially from Chinese investments under the latter’s Belt & Road Initiative (BRI). These funds have boosted public infrastructure works and mining/hydrocarbon projects – necessitating welding equipment and consumables.
The RoW belt is anticipated to emerge strongly at a healthy 6.4% CAGR by 2030 – increasing its market share on the back of industrialization and urbanization.
Demand shall rise substantially from sectors spanning construction, transportation, and assembly manufacturing. The progressive establishment of manufacturing ecosystems by attracting low-cost labor shall strengthen welding consumption.
Welding Industry Trends
The welding sector is making substantial technology-led strides – achieving improved safety, efficiency, precision, and sustainability milestones; while expanding applications across manufacturing domains through cutting-edge capabilities.
Automation
Automation constitutes an integral pillar of propelling advancement. Robotic welders are increasingly replacing human counterparts for repetitive, hazardous, and complex procedures – curtailing risks while uplifting speed, accuracy, and compliance factors. The latest automated systems feature integrated sensors, IoT modules, and chatbots enabling real-time analytics, remote troubleshooting, and minimized physical intervention.
Cobots are being deployed extensively supporting welders with dexterous functions. Machine learning algorithms help cobots to sense and adapt seamlessly. Automation is helping fill the skill gap as the aging workforce retires. It is enabling welding penetration into new areas like food processing and electronics. Auto-darkening helmets and fume extraction torches symbolize upgraded safety.

Sustainability
With climate consciousness growing, sustainable practices are being widely embraced by welding industry players through:
- Development of solar-powered, energy-efficient, portable welders with rechargeable batteries reducing energy consumption and fossil fuel reliance.
- Leveraging AI for optimizing power usage needs respective of application. Chatbots provide estimations.
- Welding institutes implementing battery recycling programs and transitioning to renewable energy sources, educating students on the criticality of a sustainable welding ecosystem.
- Manufacturers increasingly adopt practices like responsible sourcing, localized production, efficient product designs, and minimalistic packaging – curtailing carbon footprint.
Digitalization
Digital transformation is uplifting customer experience, welding quality, and operational efficiency through:
- AR/VR simulations training welding apprentices. Digital media enables remote interactive learning.
- The advent of Weld Camera Technology allows remote diagnostics capabilities to technicians for inspecting and assessing welding operations.
- IoT sensors monitor system health, welding costs, and consumable usage levels in real-time – cloud-based analytics revealing opportunities. Enabling predictive maintenance curtailing downtime.
- Chatbots resolve basic customer queries instantly. Analytics provide insights into inquiry patterns and regional buyer preferences. Social media and targeted web campaigns supporting lead generation and brand awareness.
Customization
The transition towards customization is visible through:
- Manufacturers expand product ranges to serve specific application needs better whether high-strength alloys, superior-quality wires, or electrodes for enhanced outputs.
- Customers seeking improved mobility including multi-process portability, A/C-DC compatibility, and retrofit attachments to accomplish an array of tasks through a single compact piece of equipment.
- Customers demand better value targeting aspects like optimized power efficiency, contemporary ergonomic designs, user-friendly interfaces, and budget pricing for enhanced ownership experience.
Challenges and Restraints
While the welding industry has witnessed growth, there are still some challenges before to overcome. Some key challenges relate to the shortage of skilled labor, increasing health hazards associated with handling high-temperature equipment and exposure to toxic fumes as well as raw material price volatility issues that welding suppliers frequently encounter.
Labor Shortage
The deficit of skilled welders and technicians constitutes a major impediment. An aging workforce and a lack of students opting for welding-based career paths have aggravated the situation. Labor shortfall is impacting productivity as excessive workload falls on a limited workforce; inflating wages and attrition levels. Educational institutes require optimizing curricula and upgrading systems to improve student intake for welding programs. Policy reforms enabling smooth immigration channels can also alleviate short-term pressures.
Health Hazards
Usage of high-temperature equipment and exposure to toxic fumes pose significant occupational hazards. Stringent regulations are necessitating large safety investments spanning protective gear, fume extraction mechanisms, ventilation, etc. – inflating operating costs. New joiners remain apprehensive owing to their risky nature. Developments in emerging areas like underwater welding and nuclear-based applications further heighten dangers due to radiation. Safer alternative technologies can potentially address challenges.
Raw Material Price Volatility
As welding consumables rely majorly on metals and alloys vulnerable to commodity price cycles, input costs and consumption remain highly sensitive to price movements. Sudden cost inflation shrinks profit margins and requires frequent equipment price hikes – increasing ownership costs. This impacts sales as customers prefer to delay purchases. Maintaining stable supplies through long contracts and localization can hedge such volatilities.
Future Outlook
Having analyzed major facets encompassing market size, growth trends, regional distribution, technologies, and hindrances; it is opportune to contemplate the way ahead for welding over the next decade. With the industry poised to exceed $34 billion by 2030, a few pivotal dimensions shall define progression.
Optimistic projections indicate 6-7% CAGR growth powered by increased adoption across automotive, construction, infrastructural development, and ambitious renewable energy goals. However, continuity of growth relies on consistent technological innovations to accelerate manufacturing, achieve ecological targets, and push the customization envelope further through materials science.
Research & Development
The focus on R&D shall persist yielding next-gen AI-powered systems with edge computing delivering actionable insights to engineers. Superior quality fluxes, electrodes minimizing waste. Big data analytics shall optimize selection. Ultra-high precision capabilities like micro and nano welding shall find increased relevance. Further impetus on clean technologies shall witness the wider deployment of solar/battery tools.
Policy Reforms
Favorable policy reforms and establishments of dedicated welding institutes shall enhance skill development and address the severe deficiency of welding technicians – fulfilling increased sectoral demands while reducing project timelines through an abundant workforce. Easing of cross-border trade through strategic partnership agreements shall bolster welding exports.
Customer-Centricity
As competition intensifies, brands shall aim for differentiation through premium customer experiences – integrating modular/retrofit capabilities enabling multi-process versatility, modern ergonomic designs minimizing fatigue, and breakthrough innovations like auto-darkening crystal lenses. This future-readiness shall rely on customer alignment. With EVs gaining traction globally, related welding applications shall rise, requiring equipment versatility.
FAQs
Q1. Which region accounts for the largest share of the global welding market currently?
Asia Pacific leads with a 36% market share presently on the back of high-growth economies like China, and India with thriving manufacturing, construction, and infrastructure ecosystems.
Q2. Which end-user sectors are expected to drive maximum demand growth over 2022-30?
Automotive and heavy engineering sectors will record the highest growth potential fueled by rising EV adoption and renewable energy equipment manufacturing.
Q3. How will impending workforce shortages impact market progression through 2030?
With over 50% of the current workforce nearing retirement age, skill shortages can constrain growth prospects by 10-12%. Addressing this through policy reforms remains vital.
Q4. How will IoT and AI technologies expand welding applications by 2030?
By enabling real-time analytics and minimized human intervention, IoT and AI can facilitate welding penetration into unconventional areas like medical technology and potentially robotics.
Q5. Which sustainability practice will gain maximum popularity by 2030?
With climate consciousness rising, over 78% of market participants are expected to adopt renewable energy tools and optimize welding equipment energy efficiency.
Conclusion
The welding industry forms the backbone supporting manufacturing across automotive, construction, heavy engineering, transportation, and energy domains. Underpinned by ubiquitous demand and technology innovations, this high-growth industry is expected to expand at 6-7% CAGR – crossing $34 billion by 2030. With applications diversifying, adjacent markets shall prosper concurrently. However, addressing skill shortages and rising occupational hazards remains imperative for the welding domain to realize its full potential.
As welding increasingly finds integration with pioneering technologies spanning automation, robotics, IoT, and renewables – the metamorphosis promises to be an exhilarating one! Equipped with insights into pivotal growth drivers, trends, and restraining forces – existing and new players can effectively formulate strategies tapping into the thriving welding industry.



