The welding transformer stands as one of the most fundamental components in arc welding technology, silently converting household electrical power into the specialized current needed for metal fusion.
Despite its critical role, many welders work for years without fully understanding how this electromagnetic marvel operates or why it remains indispensable in modern welding applications.
At its core, the welding transformer represents a marriage of electrical engineering and practical metallurgy.
This device takes the high-voltage, low-amperage power from wall outlets and transforms it into the low-voltage, high-amperage current that creates and maintains a welding arc. Without this crucial conversion, arc welding as we know it would be impossible.
What Is a Welding Transformer?
A welding transformer is a step-down transformer specifically designed for arc welding. It converts high-voltage, low-current power from the main supply into low-voltage, high-current electricity needed to generate a stable welding arc.
This arc forms between the tungsten welding electrode and the metal being welded, creating the heat necessary to fuse materials together.
Unlike typical power tools that run at steady outputs, welding requires quick and powerful bursts of current. A welding machine transformer is engineered to deliver this kind of energy reliably and safely, often under tough working conditions.
Its robust design allows it to handle long welding sessions without overheating or losing efficiency. These transformers are especially valued for their simplicity, durability, and ability to perform well in demanding industrial environments.
Understanding how welding transformers function helps operators select the right equipment, control weld quality, and maintain a safer work environment. For many heavy-duty applications, they remain a trusted and cost-effective solution.
How Does a Welding Transformer Work?
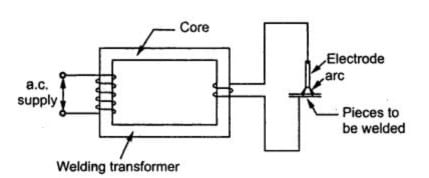
Transformers operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When alternating current flows through the primary winding, it creates a fluctuating magnetic field.
This magnetic field induces a current in the secondary winding, transforming the electrical energy from one voltage level to another.
In the context of welding, this process becomes essential. Here’s how:
- The primary coil receives high-voltage, low-current power from the main supply.
- This power is transformed into low-voltage, high-current electricity through the secondary coil.
- The resulting output is just right for creating a powerful arc between the electrode and the metal, which generates the heat needed to weld.
Welding machine transformers must be durable and efficient, often using laminated cores to reduce energy loss. Most of them deliver AC output, but many models are now equipped with rectifiers to convert that into DC, offering smoother operation and better control over the arc.
This makes transformer technology a reliable choice in many welding scenarios.
Key Components of a Welding Machine Transformer
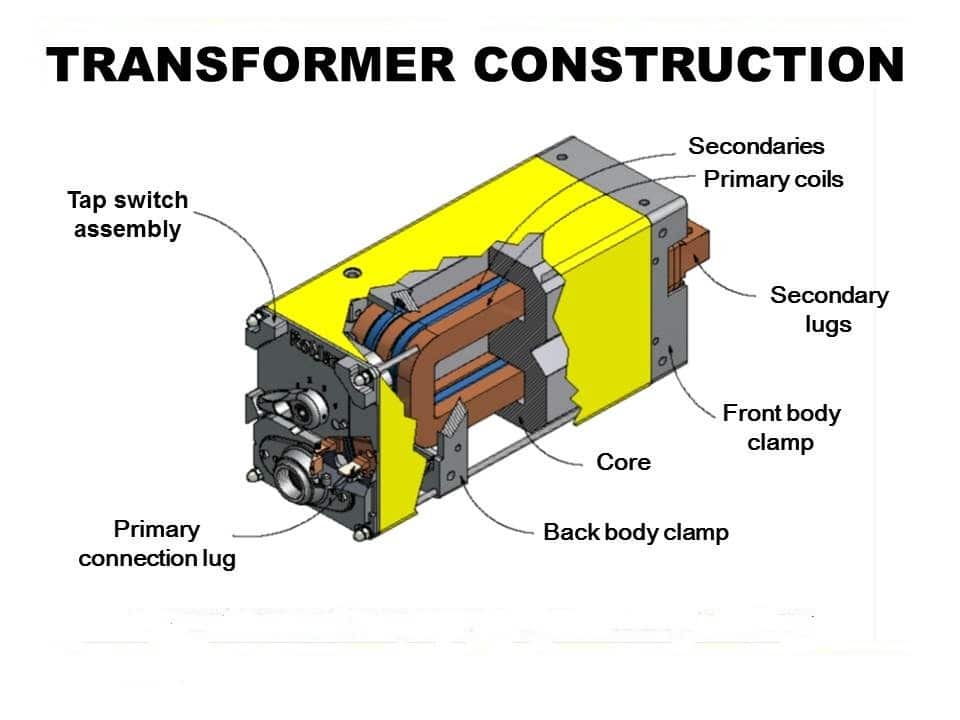
- Primary and Secondary Windings – These coils handle input and output voltage.
- Core – Usually made of laminated silicon steel to reduce energy loss.
- Taps or Reactors – Used to adjust output current.
- Cooling System – Air or oil cooling prevents overheating.
The design and material quality of these components affect how well the transformer performs in terms of efficiency, duty cycle, and arc stability.
Types of Welding Transformers
1. Air-Cooled Welding Transformers
These are compact and easier to maintain, often used for light-duty welding tasks. They rely on natural or forced air to dissipate heat.
2. Oil-Cooled Welding Transformers
Common in industrial setups, these transformers use oil as a coolant. They handle heavier loads and operate longer without overheating.
3. AC vs. DC Transformers
- AC Welding Transformers are simple and cost-effective but may lead to unstable arcs.
- DC Welding Transformers use rectifiers to convert AC into DC, providing smoother arcs and better penetration.
Advantages of Welding Transformers
Welding transformers are known for their durability, simplicity, and consistent performance. They remain widely used in industries where reliability is a priority over portability or digital features.
Key advantages include:
- Affordability: Less expensive than inverter-based alternatives.
- Durability: Fewer electronics mean lower risk of failure.
- High output: Ideal for welding thick materials with strong arc performance.
- Simplicity: Easier to operate and maintain, especially in tough environments.
Because of these traits, welding transformers are trusted in shipbuilding, construction, structural welding, and heavy machinery repair.
When used by experienced welders, these machines deliver stable arcs and strong welds, making them a cost-effective and dependable choice for heavy-duty applications.
Limitations of Transformer-Based Welders
- Bulky and heavy compared to modern inverters.
- Fixed frequency makes output less adjustable.
- More power consumption.
- Not ideal for precision work or thin materials.
That said, they’re still widely used where robustness and power matter more than portability or finesse. Learn more about Inverter vs Transformer Welders.
Applications of Welding Transformers

Welding transformers are used in:
- Shipbuilding
- Structural fabrication
- Heavy machinery repair
- Pipe welding
- Railways and infrastructure
They’re especially suitable for manual metal arc welding (MMAW) or stick welding machines, which is common in outdoor and heavy-duty environments.
Choosing the Right Welding Transformer

When selecting a welding machine transformer, consider:
- Duty cycle – How long it can operate without overheating.
- Cooling method – Air-cooled vs. oil-cooled.
- Type of metal – Thicker metals benefit from higher current.
- AC or DC output – For smoother arcs, choose DC.
- Portability – Heavier units are less mobile but more powerful.
Buying a transformer that matches your specific welding needs helps avoid underperformance or damage.
Maintenance Tips for Welding Transformers
- Keep vents and cooling fans clean.
- Periodically check winding insulation.
- Tighten connections and inspect for loose wires.
- Store in dry, dust-free environments.
- Change oil (for oil-cooled models) as per manufacturer guidelines.
Regular maintenance extends the life of your transformer and keeps performance stable.
Future Developments and Technology Trends

Electronic controls are being integrated with traditional transformer designs to provide enhanced functionality. Microprocessor-based controls can monitor transformer operation, provide diagnostic information, and adjust output characteristics for different welding processes.
Improved materials and manufacturing techniques continue to advance transformer performance. Higher-grade silicon steels reduce core losses, while improved insulation systems extend service life and operating temperature ranges.
Hybrid designs combine transformer robustness with electronic control features. These systems maintain the simplicity and reliability of transformers while adding modern features like digital displays, process selection, and remote control capabilities.
Energy efficiency improvements focus on reducing losses and improving power factor characteristics. New core materials and winding techniques can reduce no-load losses and improve overall system efficiency.
The welding transformer remains a cornerstone of arc welding technology, providing reliable, cost-effective power conversion for countless welding applications. Understanding its operation, capabilities, and limitations helps welders and fabricators make informed decisions about equipment selection and application.
As welding technology continues advancing, the fundamental principles of transformer operation will continue supporting both traditional and innovative welding processes.



