Inverter welders are advanced machines that electronically convert power, providing portability and control for welders of every experience level. Keep reading and exploring inverter welders and how they can bring welding projects to the next level!
What Is an Inverter Welder & Why it Matters

Inverter welders have surged in popularity, and it’s no surprise why. Their compact design—often weighing just 5-10 kg compared to 50 kg for traditional transformer models—makes them a go-to for everyone from construction crews to backyard DIYers.
Add to that their energy efficiency (80-90% vs. 50% for older machines), and you’ve got a tool that’s as cost-effective as it is versatile, perfect for industries like automotive repair or home fabrication.
Aside from functionality, these welders are also masters of precision. They handle thin metals with ease, like 20-gauge sheet metal, and are ideal for delicate work. And they’re kinder to the earth, sipping electricity instead of gulping it, which appeals to environmentally conscious consumers.
At introductory prices of $200, inverter welders are no longer the sole domain of pros—they’re simplifying welding into something hobbyists can do without breaking their whole paycheck.
A comparison of Inverter vs Transformer Welders may help you know better about inverter welders.
How Does an Inverter Welder Work
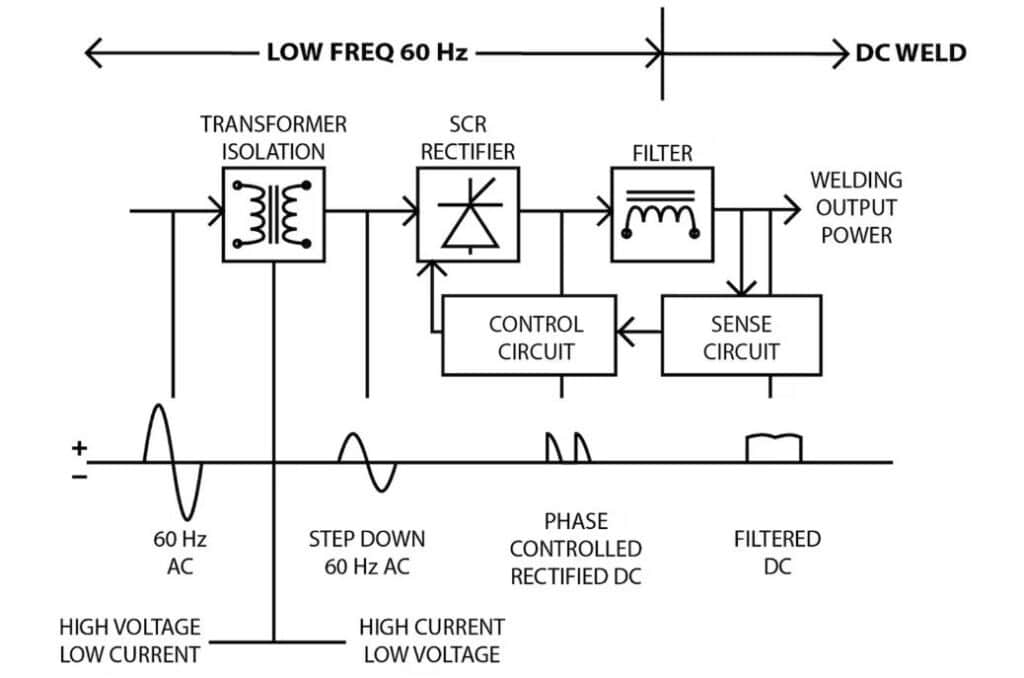
Think of an inverter welder as a power sculptor. It takes raw AC electricity (110V or 220V) and sculpts it into a stable, controlled output to weld. The process depends on electronic devices like Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs), which work like high-speed switches to sculpt power effectively.
Here’s how it breaks down:
- Rectification: AC power is converted to DC.
- Inversion: DC is switched at high frequencies (20,000-60,000 Hz) using IGBTs.
- Transformation: A small transformer lowers voltage to welding levels.
- Output Control: The system keeps the arc for smooth, stable welds.
Compared to big transformer welders, inverters have smaller components and therefore are more efficient and light.
Think sporty two-seat car vs. a lumbering truck—both get you where you’re going but one’s faster. To visualize it, think of a flow chart displaying AC waves being changed to a steady DC arc, providing cleaner welds with less spatter.
What Is an Inverter Welder Used For
Automotive Repair: Inverter welders weld thin sheet metal (like 20-gauge steel) for bodywork or exhaust systems. Their stable arcs prevent burn-through, ensuring clean patches or seams.
For example, a DIYer might use a MIG setup to restore a rusty fender, while a pro tackles chassis reinforcements with a Stick welding machine.
Home Fabrication and DIY Projects: From building a backyard gate to crafting a custom bike rack, inverter welders create durable metalwork.

Their portability (some as light as 5 kg) make it easy to weld in a small workshop or even outdoors. They can weld a steel trellis for your garden using TIG for precise, polished joints.
Construction and Structural Work: Contractors rely on inverters for on-site jobs like assembling steel frameworks or repairing heavy equipment. A Stick welding machine with an inverter handles outdoor tasks in windy conditions, while MIG tackles indoor structural beams.
Maintenance and Repair: Inverter welders are staples in maintenance shops. Their dual-voltage options (110V/220V) let you plug in anywhere, ideal for emergency repairs—like patching a cracked plow in the field.
Art and Sculpture: Artists love inverters for their finesse on delicate materials like aluminum or stainless steel. A TIG welder creates smooth, spatter-free welds for intricate sculptures. An artist might weld a 1mm steel abstract piece without warping with the inverter’s arc control.
What Are the Advantages of an Inverter Welder
Inverter welders pack features that make them stand out. Here’s what you get:
Portability
- What It Means: At 5-15 kg, these machines are easy to haul to job sites or tuck into small workshops.
- Example: A welder can carry one to a rooftop repair job without breaking a sweat.
Energy Efficiency
- What It Means: With 80-90% efficiency, they cut power bills and reduce environmental impact.
- Example: Frequent welders might save 20-30% on electricity compared to older models.
Versatility
- What It Means: They support MIG, TIG, and Stick processes, welding everything from steel to aluminum.
- Example: Switch from TIG for delicate art pieces to Stick for rugged fence repairs.
Arc Stability
- What It Means: High-frequency switching keeps arcs steady, reducing errors like spatter.
- Example: Weld 1mm steel sheets without burning through, even as a beginner.
How to Weld with an Inverter Welder
Choosing is the first step before welding with an inverter welder. 3 points that should be kept in your mind:
- Project Type: Use a MIG welding machine for general work, TIG for precision, or Stick for outdoor repairs.
- Specifications: Look for a duty cycle (e.g., 60% at 200A means 6 minutes welding per 10) and voltage compatibility (110V for home, 220V for heavy-duty uses).
- Budget: Beginner unites price is generally $200-$500, mid-range $500-$1,000, and premium $1,000-$2,000.
For instance, a DIYer fixing a car frame might grab a $300 multi-process model, while a contractor needs a $1,200 unit for daily use. Check a comparison table online to weigh options like duty cycle and weight.
Ok. Once you’ve got a welder, it’s the time to set it up.
- Setup: Plug it in, pick your process (MIG, TIG, etc.), and dial in settings based on material thickness (e.g., 100A for 3mm steel).
- Technique: Hold the torch at a 15-20° angle for MIG, keep short arc length (2-3 mm), and move steadily to avoid uneven beads.
- Practice: Test on scrap metal to get a feel for settings. Watch a quick online tutorial to see pros do it.
Take Sarah, a hobbyist who welded her own bike rack. She started with a $250 inverter, practiced on spare steel, and nailed clean welds in a weekend. Start small, and you’ll be crafting like her in no time.
What Are the Safety Precautions for Inverter Welders

A Quick Answer: Wear PPE (like welding helmets and welding gloves), ventilate your space, and inspect equipment to avoid burns, shocks, or harmful fumes.
Welding’s rewarding but demands caution:
- Gear Up: Use an auto-darkening helmet (ANSI Z87.1 certified), flame-resistant gloves, and a jacket to shield from UV rays and sparks.
- Breathe Easy: Weld outdoors or use a fume extractor to avoid gases like zinc oxide, which can cause metal fume fever.
- Check Equipment: Look for frayed wires, loose clamps, or overloaded circuits to prevent shocks or fires.
One pro tip: keep a fire extinguisher nearby. A spark can ignite debris faster than you’d think. For more, explore a welding safety checklist to stay prepared.
How to Maintain and Repair an Inverter Welding Machine
A Short Answer: Keep it clean, ensure safe connections, and store it in good condition to make it last 5-10 years.
Regular maintenance is simple but critical:
- Clean Monthly: Use compressed air to blow dust from cooling fans, preventing overheated electronics.
- Tighten Connections: Inspect cables and electrodes every 6 months, replacing anything worn.
- Store Smart: Store it in a clean, dry location to shield sensitive components such as IGBTs.
For heavy users (500+ hours/year), have a professional tune-up done once a year. A welder buddy neglected dust accumulation and fried his machine within two years—don’t do that. An easy maintenance cycle saves money and trouble.
Wrapping Up
Inverter welders blend portability, efficiency, and precision, making them a must-have for welders tackling projects big or small. By mastering their features, prioritizing safety, and budgeting wisely to choose proper machines from welding machine suppliers, you’re set to create with confidence.
FAQ
What is an inverter welder and how is it different from a transformer welder?
An inverter welder uses advanced electronic components to convert AC power into a stable DC output. Unlike traditional transformer welders, they are lightweight, energy-efficient, and offer greater control over arc stability.
What types of welding can inverter welders handle?
Most inverter welders support multiple processes, including MIG, TIG, and Stick welding, allowing you to work on a wide range of materials like steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Are inverter welders more energy-efficient than traditional welders?
Absolutely. Inverter welders operate at 80–90% efficiency, compared to 50% for traditional models, meaning lower electricity costs and a smaller environmental footprint.
Can inverter welders handle heavy-duty projects?
Yes, mid to premium inverter models with higher amperage and duty cycles can easily tackle industrial or contractor-grade tasks.
What voltage do inverter welders use?
Many models are dual-voltage (110V/220V), making them versatile for both home workshops and commercial sites.



