The automotive welding industry is a highly technical and demanding field that utilizes welding technology, integrating the art of skilled craftsmanship with the science of sophisticated metallurgy in the production, repair, and rebuilding of automobiles. There is automotive welding cranking out cars on assembly lines of big manufacturers, as well as in custom job shops to restoration service garages. Automotive welding is the kernel of the automotive industry, with welders needing to learn a variety of processes in various types of materials using strict specifications.
Welding in the vehicle industry entails a lot more than just joining metals. All the welds need to satisfy the strictest safety requirements, withstand corrosion, and deal with extreme stress, while also sometimes enhancing the aesthetic value of the vehicle. A combination of these unique requirements makes automotive welding a very specialized area that has attracted the attention of competent professionals who find exciting and well-paid careers.
The vocation of automotive welding can be perceived as being technical in an advanced way, as well as being very crucial in vehicle safety and performance. Are you a prospective automotive welder, a person interested in the manufactory processes, or a plain old curious? We have a complete guide covering details of everything relating to such an exciting profession.
The Foundation of Automotive Welding
Automotive welding covers all welding processes used in vehicle manufacturing, repair, modification, and restoration. Unlike general metal fabrication, it must address unique challenges such as:
- Working with thin sheet metals prone to warping.
- Handling complex geometries in vehicle structures.
- Joining dissimilar metals (e.g., steel with aluminum).
- Meeting strict quality and safety standards to ensure passenger protection and vehicle durability.
Main Categories of Automotive Welding
- Production Welding – Large-scale, high-volume manufacturing where automation, speed, and consistency are critical.
- Repair Welding – Focuses on restoring damaged vehicles while keeping safety and original specifications intact.
- Custom Fabrication – Involves unique builds and modifications, requiring creativity and technical precision.
- Restoration Welding – Specialized in vintage vehicles, using period-accurate materials and historical techniques.
Evolution of Automotive Welding
- Early vehicle welding relied on basic steels and simple joints.
- Modern welding must deal with:
Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS) for safety and lightweight design.
Aluminum alloys and composites for fuel efficiency.
Emerging materials like carbon fiber and magnesium.
- Welders also need to manage sensitive electronic systems in modern cars, making electrical isolation and shielding techniques essential.

Welding Processes in Automotive Applications
Different welding processes serve specific roles in automotive manufacturing and repair, each offering unique advantages for particular applications. Understanding these processes is fundamental to comprehending modern automotive welding.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (MIG)
Gas Metal Arc Welding (MIG) dominates automotive production due to its speed, versatility, and ability to produce clean, spatter-free welds. MIG welding excels at joining thin sheet metal components, making it ideal for body panels, structural elements, and exhaust systems. The process allows for precise heat control, minimizing distortion in thin materials while providing strong, durable joints. Short-circuit MIG welding enables welders to work on materials as thin as 24-gauge steel without burn-through, while spray transfer techniques provide deep penetration for thicker structural components.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (TIG)
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (TIG) serves as the precision tool of automotive welding, particularly valuable for aluminum components, stainless steel exhaust systems, and high-end custom work. TIG welding produces the highest quality welds with exceptional control over heat input, making it essential for repairing expensive aluminum body panels or fabricating custom components where appearance and strength are equally important. The process requires significant skill development but offers unmatched versatility for working with diverse materials and thicknesses.

Resistance Spot Welding
Resistance Spot Welding forms the foundation of automotive assembly, with modern vehicles containing thousands of spot welds joining body panels and structural components. This process uses electrical resistance to generate heat, creating welds without filler material in a fraction of a second. Spot welding enables high-speed production while providing consistent, reliable joints that meet strict strength requirements. Understanding spot welding principles is crucial for anyone working in automotive repair, as these welds often require specialized equipment and techniques to replicate properly.
Laser Welding
Laser Welding represents the cutting edge of automotive manufacturing, offering precision and speed unmatched by traditional processes. Major manufacturers increasingly use laser welding for critical structural components, where its ability to create narrow heat-affected zones and deep penetration welds provides superior strength-to-weight ratios. While primarily used in production environments, understanding laser welding helps automotive professionals appreciate modern vehicle construction and repair requirements.
Materials and Metallurgy in Automotive Welding
The materials used in modern vehicles present unique challenges that distinguish automotive welding from other applications. Each material requires specific welding techniques, filler metals, and post-weld treatments to achieve optimal results.
Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS)
Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS) now comprise significant portions of modern vehicle structures, offering improved crash protection while reducing weight. These steels require careful heat management during welding to maintain their specialized microstructures and mechanical properties. Welding AHSS demands understanding of cooling rates, heat-affected zone properties, and proper filler metal selection to avoid creating weak points in critical safety structures.
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum usage in automotive applications continues to expand as manufacturers seek weight reduction for improved fuel efficiency. Aluminum welding presents unique challenges, including oxide formation, high thermal conductivity, and susceptibility to hot cracking. Automotive aluminum welders must master techniques for cleaning, joint preparation, and heat management while working with alloys specifically designed for automotive applications.
Galvanized Steel
Galvanized Steel provides corrosion protection but creates welding challenges due to the zinc coating that can cause porosity and toxic fumes. Automotive welders must understand proper ventilation requirements, coating removal techniques, and methods for maintaining corrosion protection around weld areas. Many modern vehicles use zinc-coated steels throughout their structure, making these skills essential for professional automotive welders.

Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel appears primarily in exhaust systems, where its corrosion resistance and high-temperature properties provide long service life. Welding stainless steel requires an understanding of carbide precipitation, heat tinting, and proper filler metal selection to maintain corrosion resistance. Many automotive applications also require specific aesthetic considerations for visible welds.
Essential Skills and Techniques
Successful automotive welding requires mastering numerous specialized techniques beyond basic welding skills. These techniques address the unique challenges of working in confined spaces, on thin materials, and with complex assemblies.
Distortion Control
Distortion control ranks among the most critical skills in automotive welding. Thin sheet metal readily warps under welding heat, potentially affecting fit, finish, and structural integrity. Automotive welders develop techniques, including proper joint design, sequence welding, heat sinks, and fixture use, to minimize distortion while maintaining weld quality. Understanding thermal expansion and contraction helps welders predict and compensate for material movement during welding.
Access welding skills enable welders to create quality joints in the confined spaces typical of vehicle construction. Automotive welders must adapt their techniques for welding through small openings, around obstacles, and in positions where standard welding approaches won’t work. This requires creativity, specialized equipment, and extensive practice to maintain quality standards in challenging positions.
Appearance welding techniques ensure that visible welds meet aesthetic standards while maintaining structural integrity. Custom automotive work often requires welds that serve as design elements, demanding skills in consistent bead appearance, smooth transitions, and artistic application of welding processes.

Safety Considerations and Best Practices
Automotive welding presents unique safety challenges that require specialized knowledge and precautions beyond standard welding safety practices. Understanding these hazards protects both welders and the vehicles they work on.
Electrical system protection is crucial when welding on modern vehicles containing sensitive electronic components. Improper welding practices can damage expensive control modules, airbag systems, and sensors. Automotive welders must understand proper grounding techniques, electrical isolation methods, and component protection procedures to avoid costly damage while performing welding operations.
Fire prevention requires special attention in automotive environments where flammable materials, including fuel, oil, upholstery, and sound deadening material, create fire hazards. Proper preparation, fire watch procedures, and emergency response plans are essential components of safe automotive welding practices.
Ventilation requirements become more complex in automotive applications due to the variety of coatings, adhesives, and materials that may release toxic fumes when heated. Automotive welders must understand the hazards associated with galvanized coatings, paint systems, and sound deadening materials, implementing appropriate ventilation and respiratory protection.

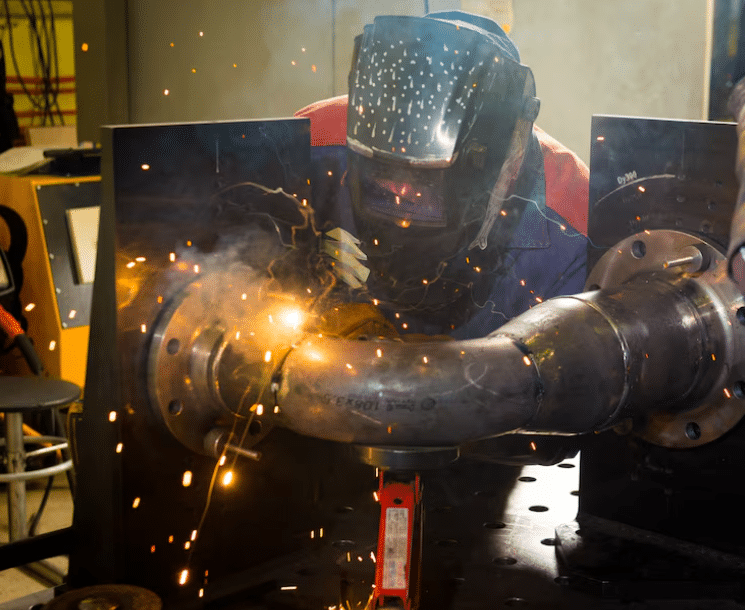
Career Opportunities and Industry Applications
The automotive welding field offers diverse career paths ranging from production line work to highly specialized custom fabrication. Understanding these opportunities helps individuals choose paths aligned with their interests and goals.
Manufacturing welding positions offer stability and benefits in automotive production facilities. These roles typically involve specialized equipment, high production volumes, and standardized procedures. Manufacturing welders often specialize in specific processes or components, developing expertise that makes them valuable to employers and provides advancement opportunities into supervisory or technical roles.
Collision repair welding combines technical skills with customer service in a growing field. Collision repair welders must understand multiple processes, work with insurance requirements, and often handle a variety of makes and models. This field offers entrepreneurial opportunities and the satisfaction of restoring damaged vehicles to original condition.
Custom automotive fabrication attracts welders interested in creative expression and unique challenges. This field includes hot rod building, race car construction, and custom vehicle modification. While potentially lucrative, custom work requires business skills, artistic ability, and extensive technical knowledge across multiple processes and materials.
Restoration welding serves the growing classic car market, requiring historical knowledge and specialized techniques. Restoration welders must understand period-appropriate materials and methods while meeting modern safety standards. This niche field often provides the satisfaction of preserving automotive history while commanding premium rates for specialized skills.
Tools and Equipment Requirements
Automotive welding demands specialized equipment designed to handle the unique requirements of vehicle construction and repair. Understanding these tools helps professionals make informed equipment decisions and appreciate the investment required for quality automotive welding.
Multi-process welders provide the versatility needed for diverse automotive applications. Modern machines offering MIG, TIG, and stick capabilities allow welders to handle various materials and situations with a single power source. Features like pulse capabilities, advanced wave forms, and precise heat control specifically benefit automotive applications.
Specialized accessories, including spot welding attachments, plasma cutters, and forming equipment, extend welder capabilities for automotive work. These tools often represent significant investments but enable welders to handle complex repairs and fabrication projects efficiently.
Measurement and fit-up tools ensure proper alignment and dimensions in automotive welding. Precision is crucial in vehicle construction, making quality measuring tools, fixtures, and alignment equipment essential for professional results.
Closing Thoughts
Automotive welding is one of the most demanding yet rewarding applications of welding technology, blending technical expertise with craftsmanship and strict safety standards. Success in this field requires mastering multiple processes, understanding different materials, and applying specialized techniques while adapting to the increasing complexity of modern vehicles.
As the industry advances toward electric vehicles, lightweight alloys, and automated manufacturing, skilled welders who embrace continuous learning will find abundant opportunities. Automotive welding remains both an art and a science, offering career satisfaction, strong earning potential, and the pride of contributing to the vehicles that power our modern world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1:Can you weld on a car with the battery connected?
It’s strongly recommended to disconnect the battery before welding on a car. Welding with the battery connected can send electrical surges through the vehicle’s circuits, potentially damaging sensitive electronic systems such as ECUs, sensors, or airbag modules. Always remove or isolate the battery and follow grounding best practices for safe automotive welding.
Q2:What type of welder is best for beginners in automotive welding?
For beginners, the best welder for automotive welding is usually a MIG welder. MIG welding is easier to learn, faster, and ideal for working with thin sheet metal commonly found in car bodies. While TIG welders produce cleaner and stronger welds—especially for aluminum and stainless steel—they require more skill and practice, making them better suited for advanced welders.
Q3:Can automotive welding be done at home?
Yes, DIY car welding can be done at home if you have the right equipment and follow strict safety measures. A compact MIG welder, protective gear, proper ventilation, and a safe workspace are essential. However, for structural repairs or work on modern vehicles with sensitive electronics, it’s often better to seek professional help rather than attempting home automotive welding.



